Personal Application Center
What is an Agent
What is an Agent?
An Agent refers to an intelligent program or system with autonomous perception, understanding, reasoning, and execution capabilities. It can independently formulate plans, invoke tools, execute tasks based on user-provided goals, and even dynamically adjust its behavior according to feedback during the task process, ultimately achieving goals efficiently.
Unlike traditional software programs that rely on manual step-by-step operations, an Agent can "think and act" on behalf of the user, thus realizing a complete task loop of "instruction-driven → autonomous decision-making → automatic execution."
Core Characteristics of an Agent
- Goal-oriented: Clearly defines task objectives and formulates strategies based on user instructions or context.
- Autonomous behavior: Possesses a certain degree of initiative and autonomy, capable of independently executing complex tasks without step-by-step guidance.
- Environmental perception and feedback: Able to obtain information from external systems, data sources, or user inputs, and dynamically adjust execution paths accordingly.
- Tool invocation capability: Can flexibly call external resources such as search engines, databases, APIs, automation tools, etc., to complete required operations.
- Continuous learning and optimization: Some advanced Agents have continuous learning and optimization capabilities, improving performance over long-term use.
Analogous Example
- You can think of traditional software as a "toolbox," where each function requires manual clicking and operation;
- An Agent is more like a "skilled assistant," where you only need to tell it "what I need to accomplish," and it can decide which tools to use, in what order, and how to handle unexpected situations to ultimately achieve the goal.
Application Scenarios
Intelligent assistants are widely applied across multiple business domains. Typical scenarios include:
-
Enterprise Automation Office
- Automatically drafting daily reports, weekly reports, meeting minutes, emails, etc.
- Automatic schedule management and meeting coordination
- Automatic data analysis and generation of charts and conclusion reports
-
Financial Services and Risk Management
- Automatically generating compliance or audit reports
- Risk sentiment monitoring and anomaly event identification
- Automated customer risk assessment and credit scoring
How to Create a Personal AI Studio
Basic Agent Creation
-
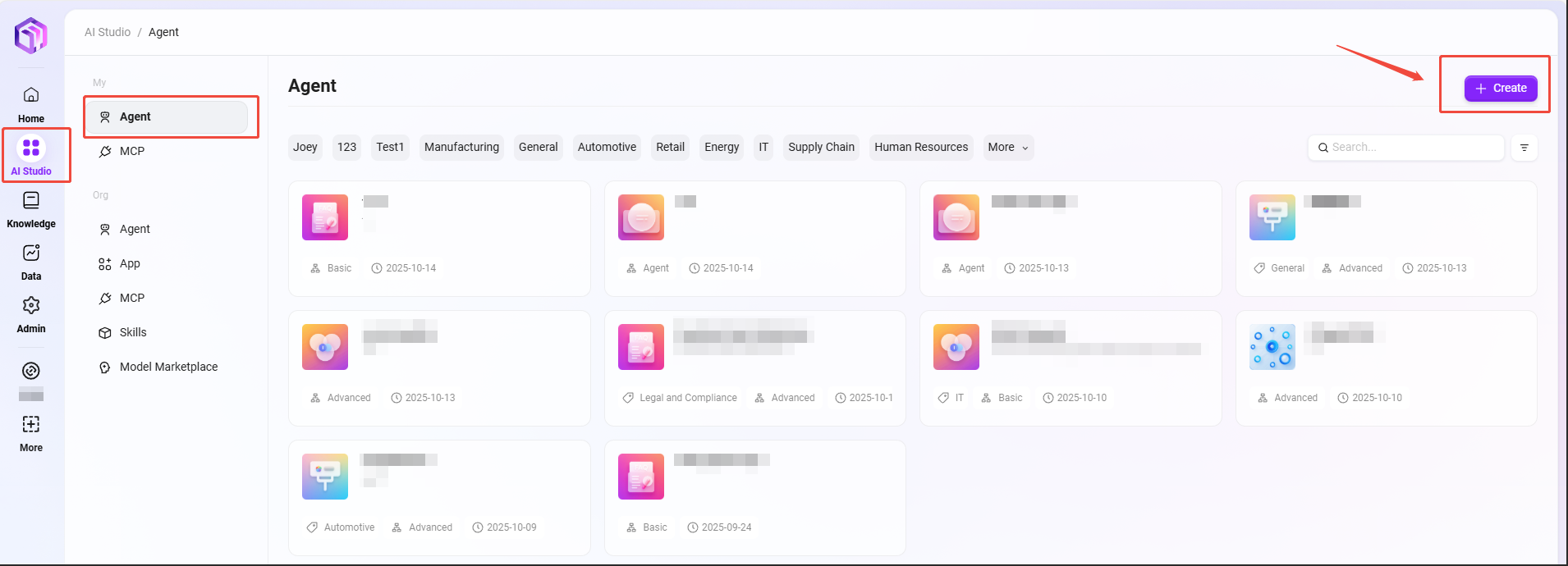
On the AI Studio page, click "Create" at the top right corner to create a basic Agent.
-
Creation steps
-
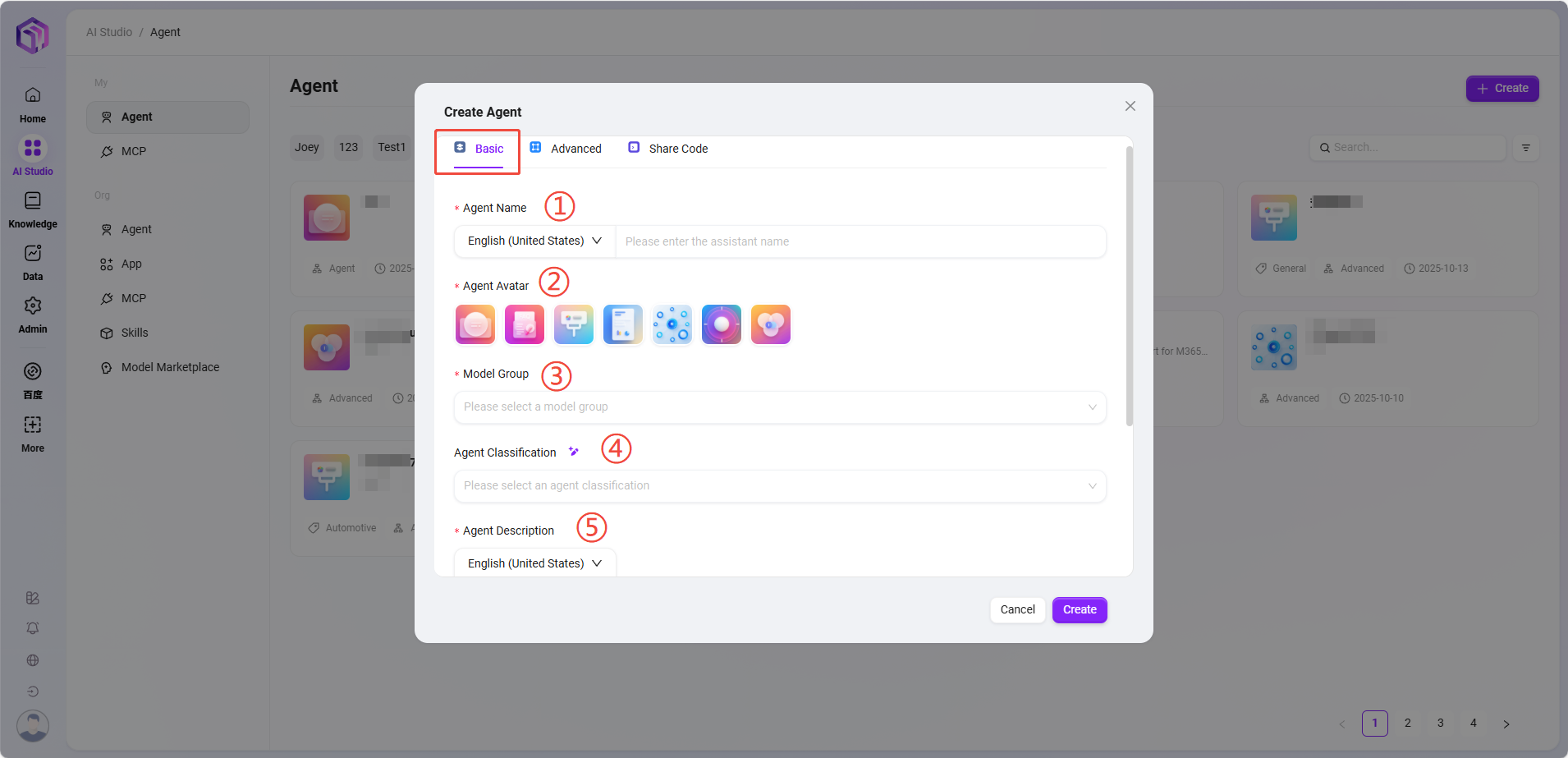
Enter assistant name, select assistant avatar, choose model group, select assistant category, add assistant description:
① Assistant Name: Enter the name of the assistant as its identifier.
② Assistant Avatar: Select the default avatar for the assistant; uploading avatars is currently not supported.
③ Model Group: Configure an appropriate model group for the assistant.
④ Assistant Category: Select the group(s) where the new assistant belongs; multiple selections allowed.
⑤ Assistant Description: Enter a brief description explaining the assistant's functions and purposes. -
Click "Create"; after creation, the assistant enters the basic orchestration configuration page. Configure and publish to put it into use.
-
- Assistant Configuration
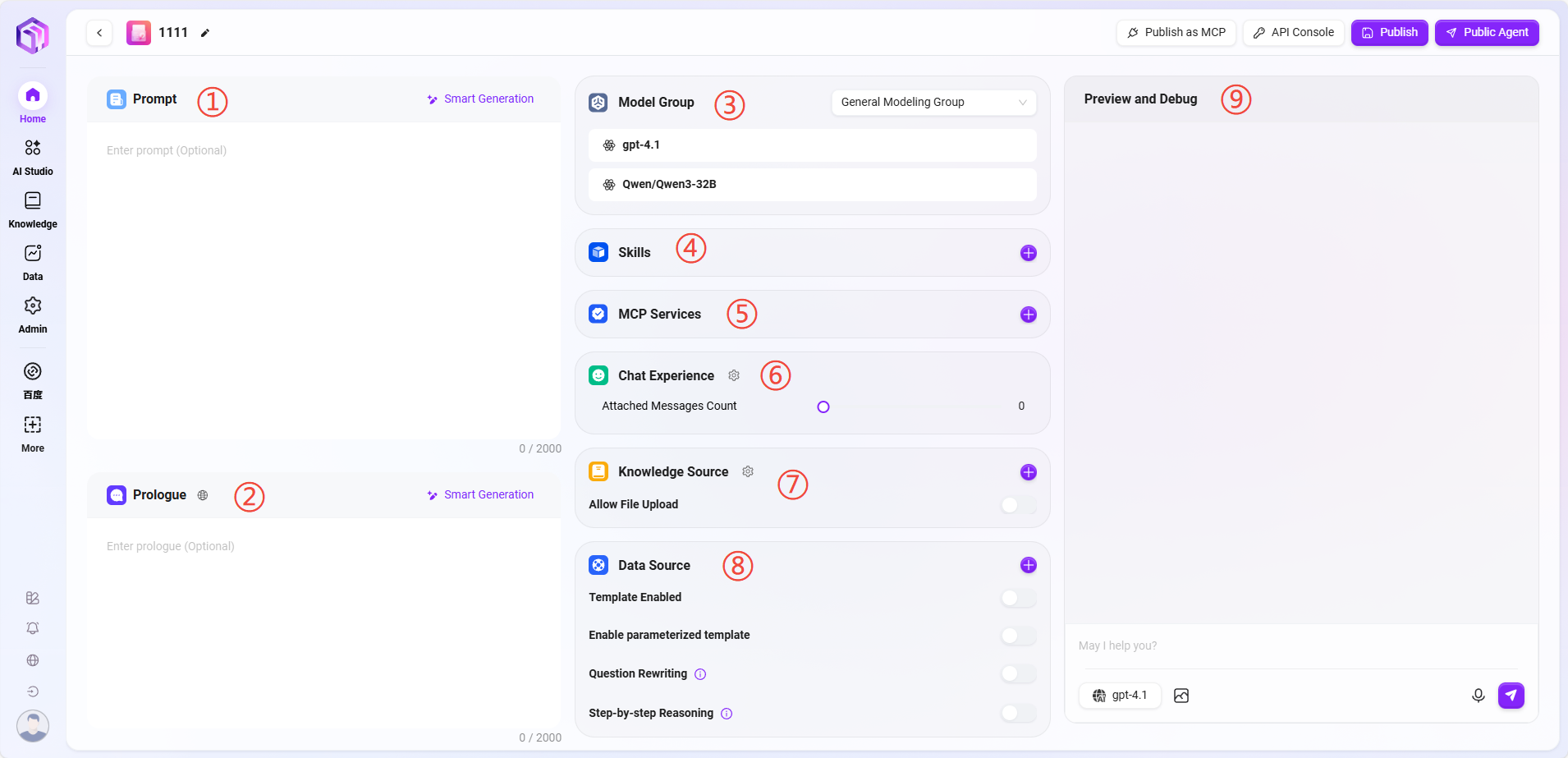
There are two ways to enter assistant configuration:
-
Directly enter the configuration page after creating the assistant;
-
Hover the mouse over the assistant card to see the "✏️" icon, click it to enter the configuration page.
① Prompt: Enter the assistant prompt; intelligent generation of prompts from existing ones is supported. Prompt length limit is 2000 characters.
② Opening Statement: Enter the assistant's opening statement; intelligent generation based on prompts or existing opening statements is supported. Opening statement length limit is 2000 characters.
③ Model Group: Click "+" to add model groups; multiple models are supported.
Note: Model groups must first be added by administrators in system management by grouping multiple different models into one model group, which is then configured to the assistant.
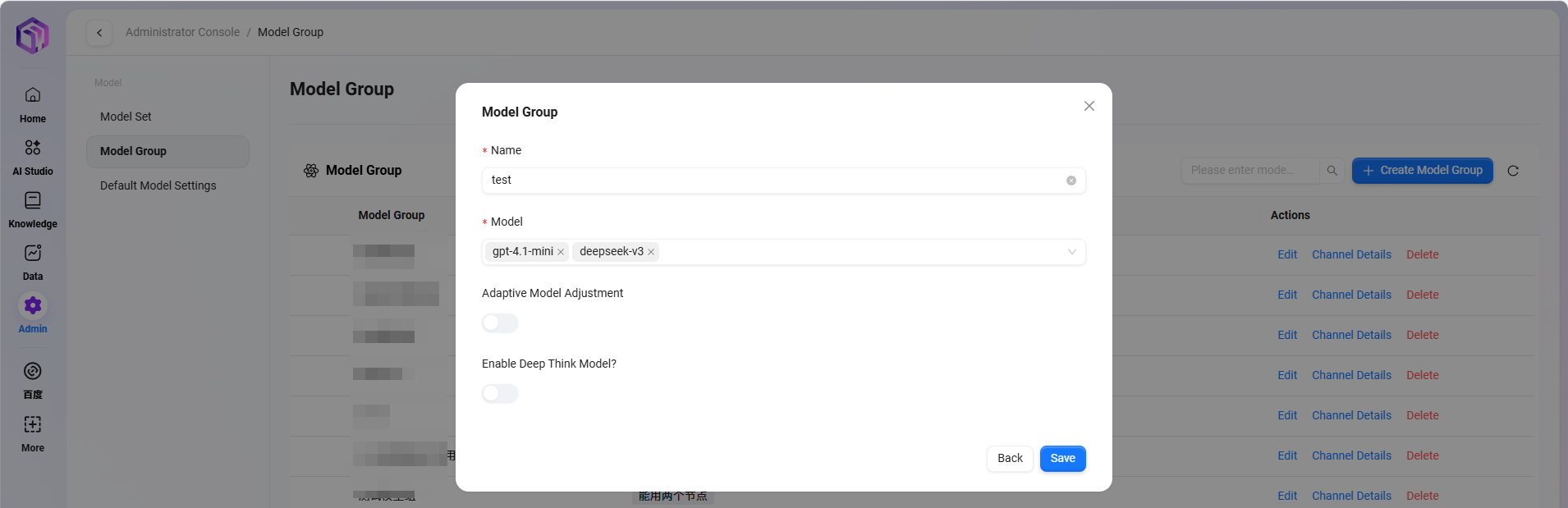
Adding Model Groups
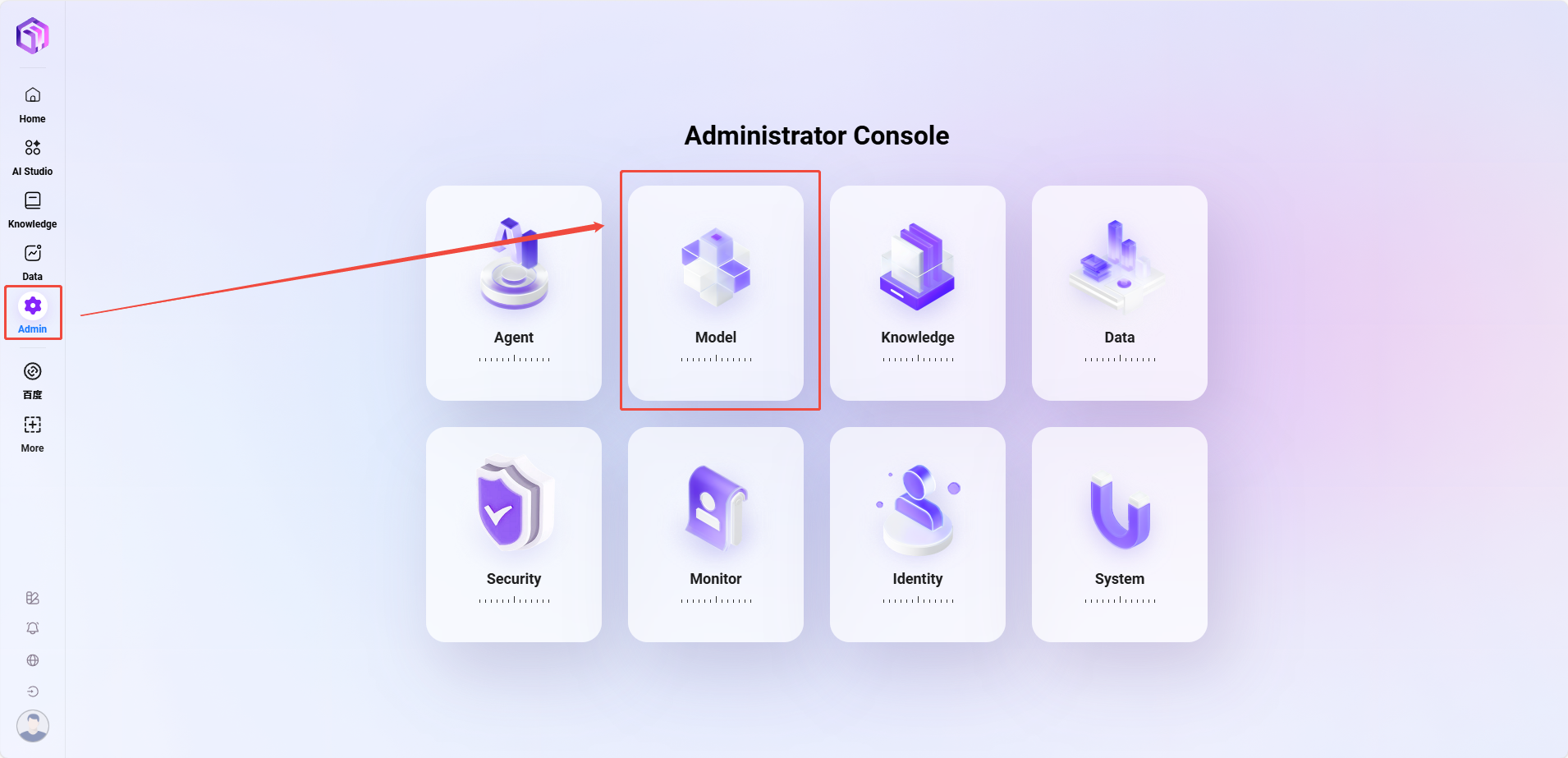
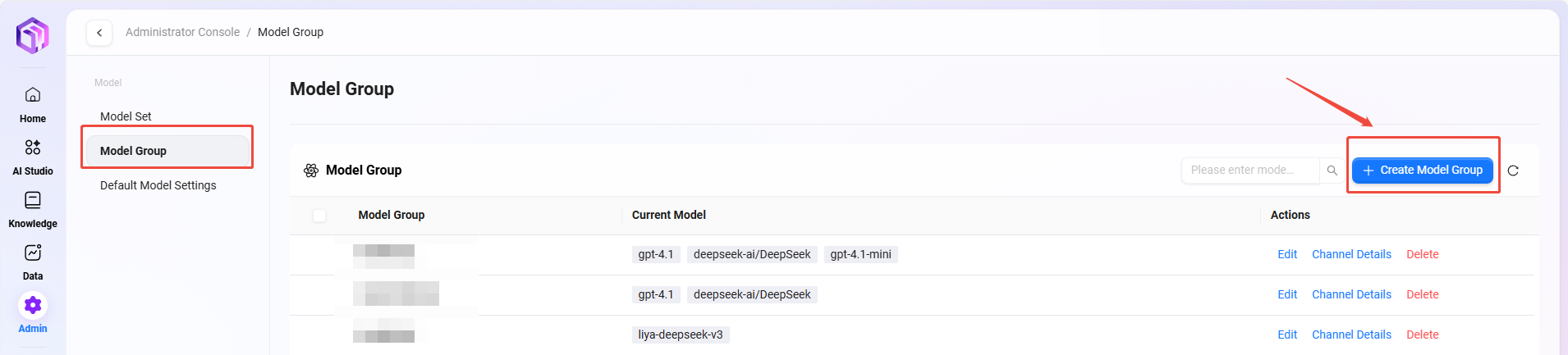
-
Path: Management → Model Management → Model Groups → Create Model Group (only administrators can add models)
-
Steps to add:
- Click "Create Model Group"
- Complete the following configurations:
- Enter model group name
- Select models to add to the group; multiple selections allowed
- Choose whether to enable adaptive model deployment
- Choose whether to enable deep thinking model
- Click "Save"
-
Adaptive Model Deployment: Automatically adjusts computing resources based on traffic to ensure stable and smooth service;
-
Deep Thinking Model: Intelligently invokes more powerful AI for complex problems, significantly improving answer quality.
④ Skills: Click "+" to add one or more skills, or add recommended skills.
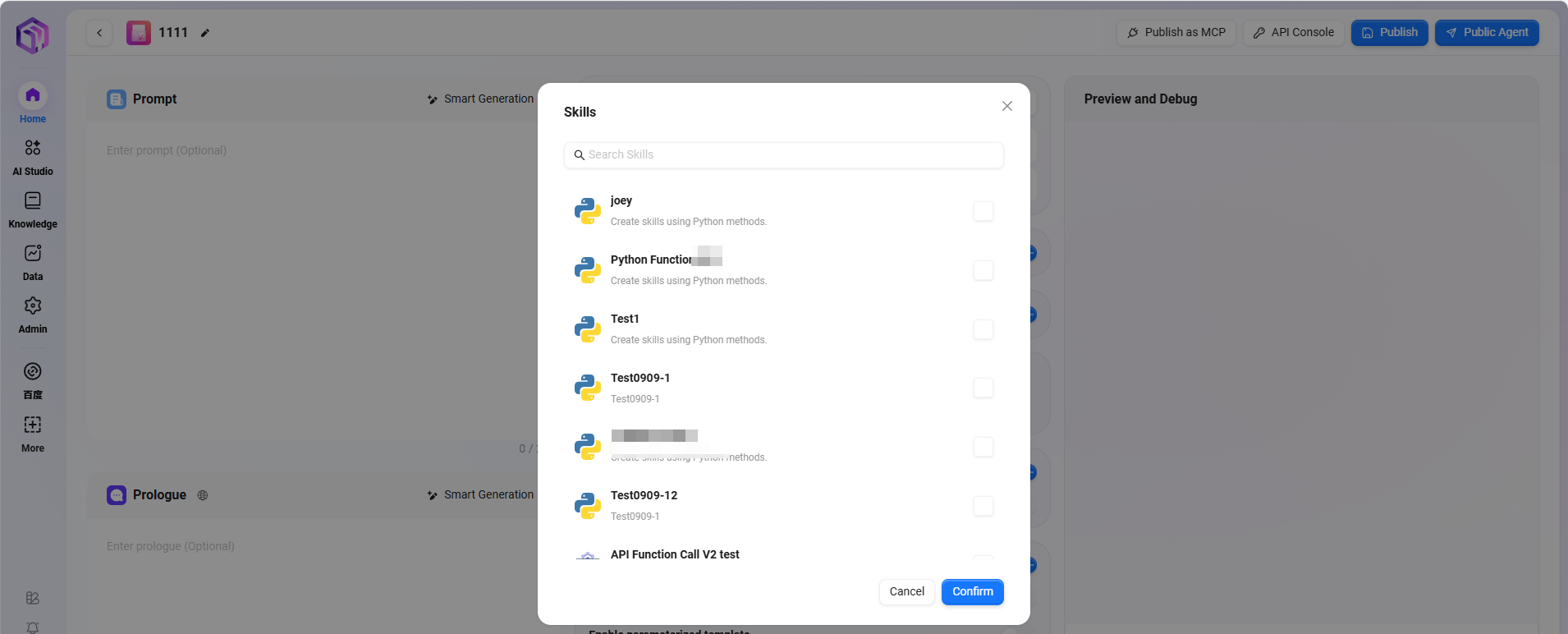
There are 5 default skills: Google Search, Tencent Search, Text-to-Image, News Query Tool, Webpage Reader.
- Google Search: Retrieves real-time, accurate web information via Google search engine, supporting global webpage content retrieval.
- Tencent Search: Based on Tencent search technology, provides search services optimized for the Chinese internet environment, especially for Chinese content retrieval.
- News Query Tool: A dedicated tool for searching and obtaining various news information.
- Webpage Reader: Extracts webpage text, data, and parses webpage information.
- Text-to-Image: Automatically generates corresponding images based on text descriptions, turning textual creativity into visual presentation.
Note: Additional skills can be appended, requiring administrator operation and configuration.
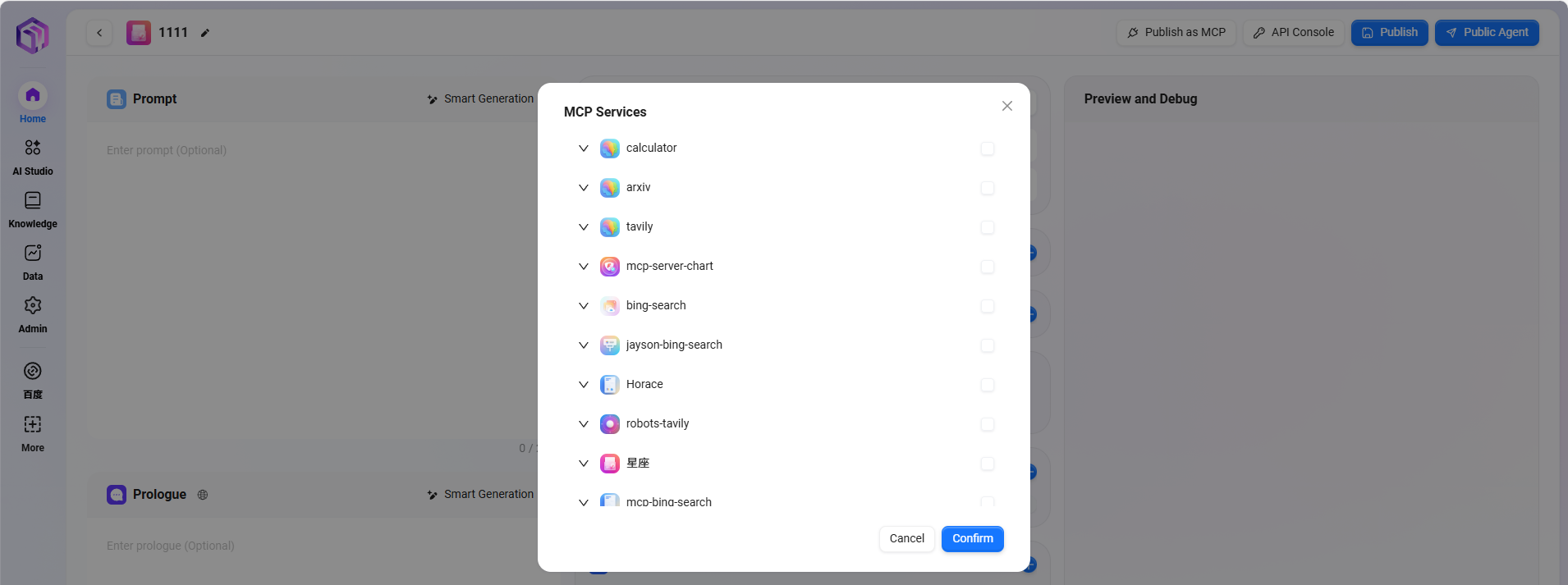
⑤ MCP Service
-
MCP service manages AI assistant's connection permissions with external tools and data sources
- Capability Extension: Enables AI assistants with practical functions such as search, computation, visualization.
- Rich Ecosystem: Continuously integrates various tool services to meet diverse needs.
- Standardized Access: Integrates internal system resources through personal MCP.
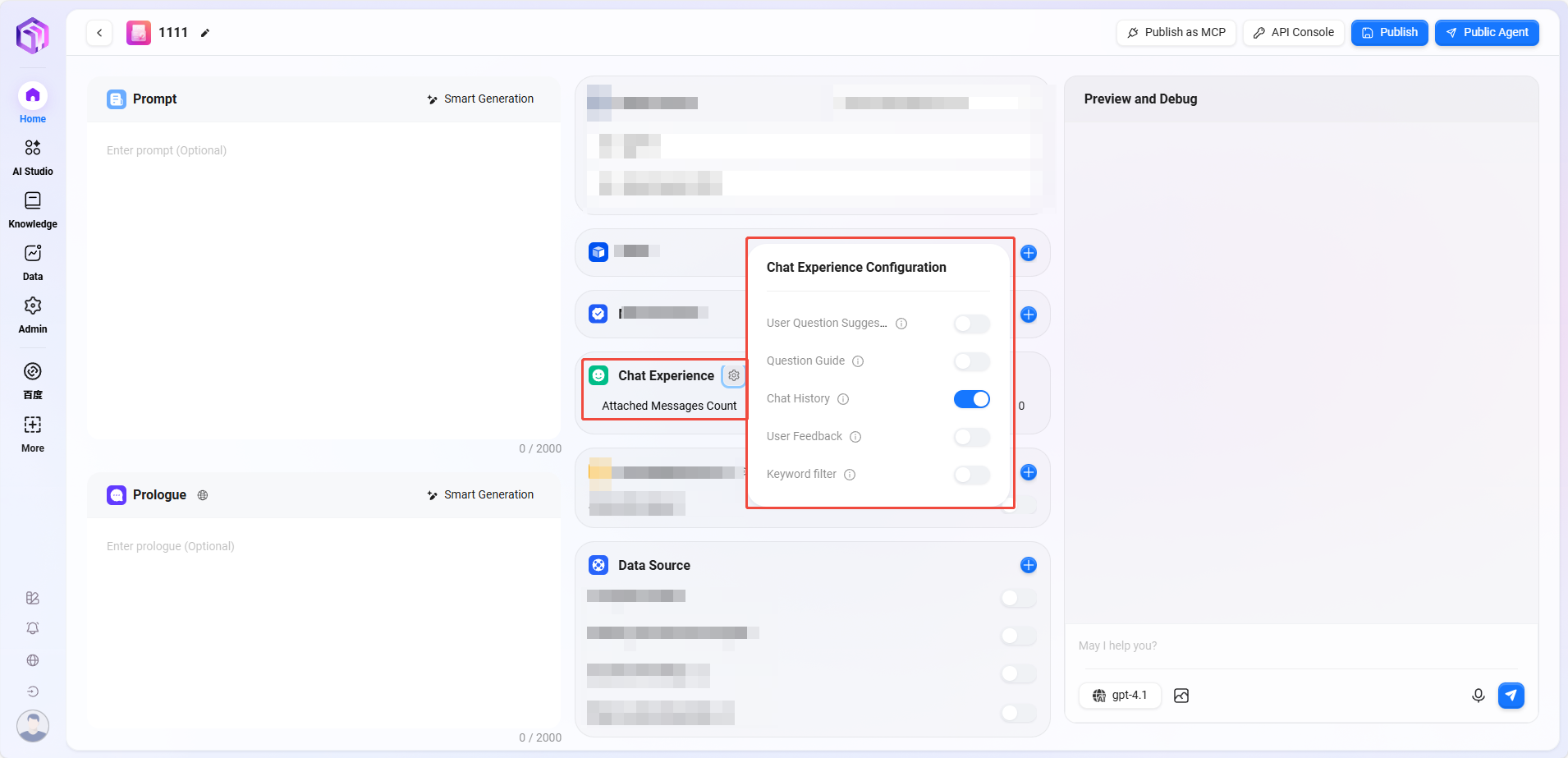
⑥ Conversation Experience:
- Conversation Settings: Can enable settings such as "User Question Suggestions, Question Guidance, Chat History, Conversation Feedback, Keyword Review"
- User Question Suggestions: After the assistant answers, provides some question suggestions to the user based on previous context.
- Question Guidance: During user-assistant conversations, relevant question guidance appears, leveraging model capabilities to infer possible user questions and complete user queries.
- Chat History: Whether to retain assistant chat history; if disabled, chat history cannot be retrieved.
- Conversation Feedback: Allows interactions such as likes or dislikes on assistant answers to optimize responses.
- Enable Keyword Review: At least one of input content review or output content review must be enabled. Once enabled, sensitive word detection is performed on prompts or AI feedback results; sensitive words can be maintained in advance.
⑦ Knowledge Base:
- Knowledge Base: Click "+" to add a knowledge base
- Allow File Upload:
- If enabled, knowledge base content cannot be added as a knowledge source
- If disabled, personal or enterprise space knowledge bases can be selectively added as knowledge sources
- Allow File Upload:
- Knowledge Base Configuration: Modify detailed settings such as "Retrieval Strategy, Private Domain Q&A, Retrieval Method"
-
Retrieval Strategy: Hybrid Search, Embedding Search, Text Search
- Hybrid Search: Combines vector retrieval and full-text retrieval results, returning reranked results
- Embedding Search: Finds fragments by similarity, with some cross-language generalization ability
- Text Search: Finds fragments by keywords, suitable for retrieval containing specific keywords or noun phrases
-
Maximum Recall Count: Range 1–10; not recommended to set too high or too low; recommended value is 3–5
-
Metadata Filtering: None, Filter, Weight
-
Force Private Domain File Q&A: When enabled, network search and other skills are not used; assistant answers only based on knowledge base content
-
Document Matching Similarity: Range 0–1; higher similarity means recalled document content is more similar; recommended value about 0.8 (80%)
-
QnA Matching Similarity: Range 0–1; similar to document content similarity matching; recommended value about 0.9 (90%)
-
Show References: When enabled, the assistant lists referenced documents in answers to improve credibility
-
💡 Tip: Neither maximum recall count, document matching similarity, nor QnA matching similarity is better the higher or lower; set according to actual needs. If no special requirements, keep default values.
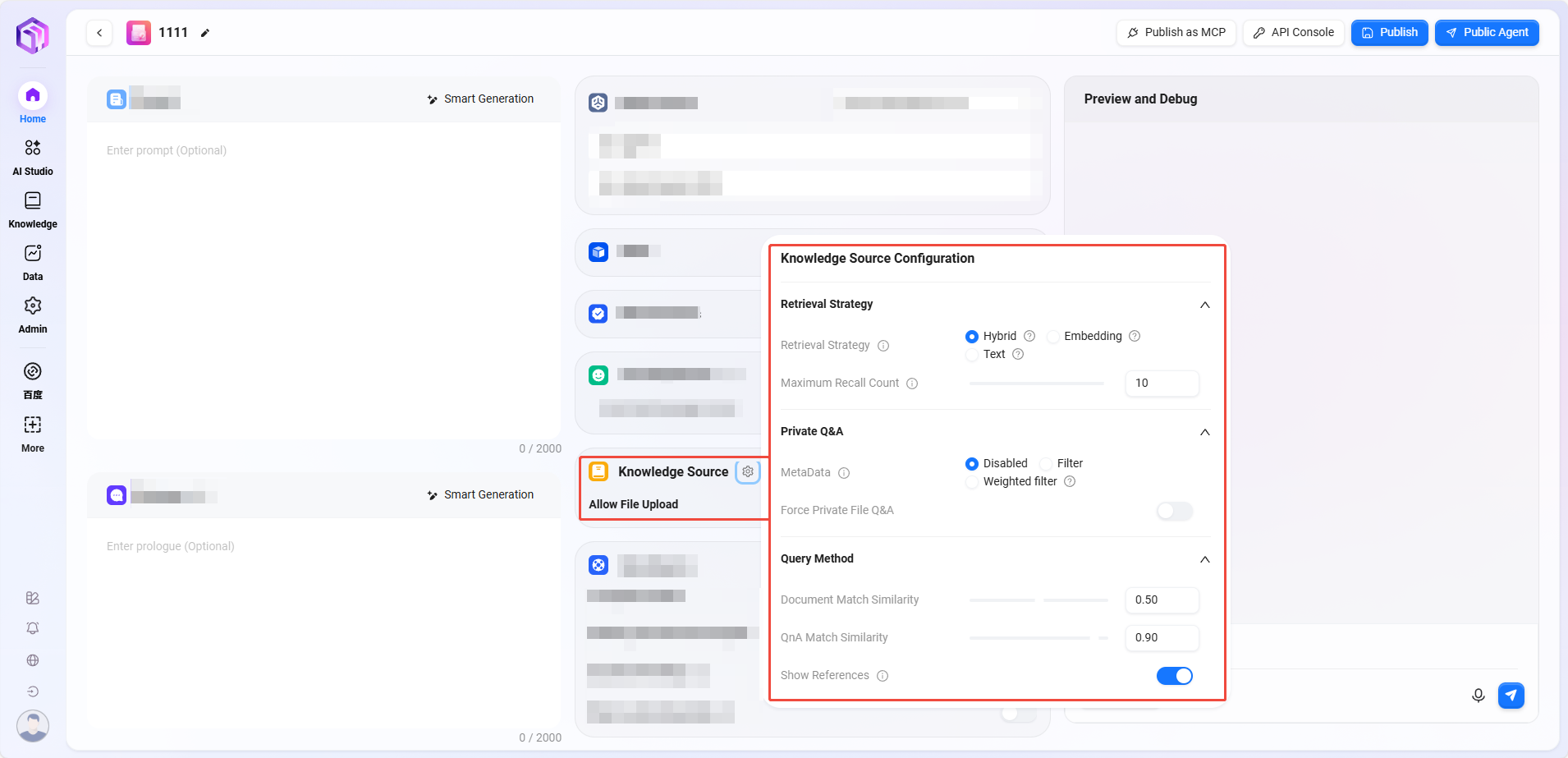
⑧ Data Source
-
Data Source: Click "+" to add data sources as assistant Q&A data sources
-
Enable Template: Whether to enable preset mapping templates between natural language and SQL.
- When a user inputs a natural language question (e.g., "
What was last month's sales?"), the system first tries to match a preset template. - If a matching template is found (e.g., a general question like "
Query sales for a certain period"), the existing SQL structure in the template is used as a reference, combined with specific fields/table names to generate the final SQL statement.
- When a user inputs a natural language question (e.g., "
-
Enable Parameterized Template: When enabled, parameterized queries are activated on the template basis, enhancing query flexibility and security.
-
Question Rewriting: When enabled, automatically optimizes user input questions to ensure accurate data queries
- User original question:
Check sales(incomplete information) - After rewriting:
Query total sales of all products in July 2024(added time and scope)
- User original question:
-
Step-by-step Thinking: When enabled, before generating the final query result, the system outputs detailed reasoning steps explaining how it analyzes the question and constructs the SQL query.
- Step 1: Identify keywords "
July 2024" and "sales" - Step 2: Determine data table
Orders, fieldsorder_dateandsales_amount - Step 3: Construct date range condition
2024-07-01to2024-07-31 - Step 4: Generate SQL
- Step 1: Identify keywords "
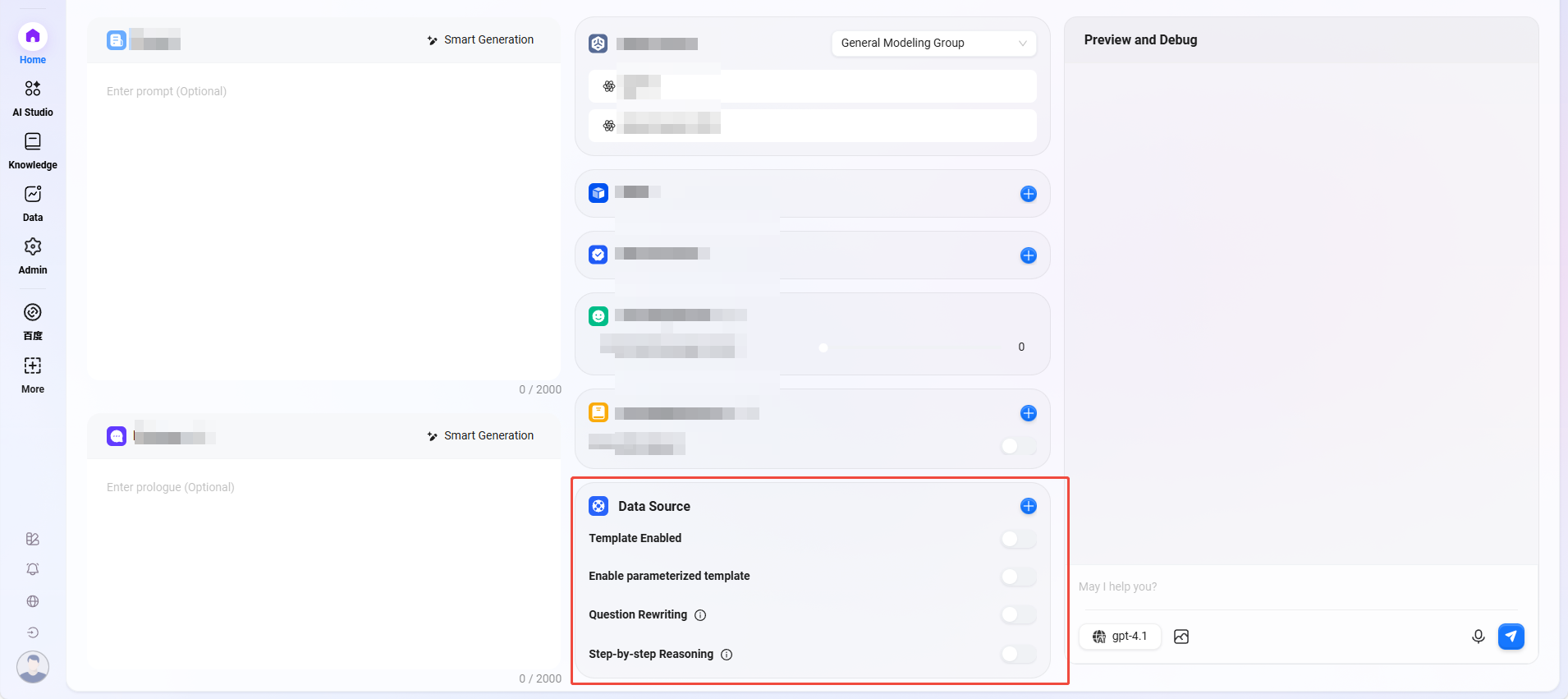
Workflow Agent Creation
- Select "Advanced Agent" (creation steps same as creating a normal agent)
- Build Types
- Advanced Mode: Quickly build complex workflows to precisely meet business needs.
- Application Mode: Create complete, advanced orchestration applications with user-friendly interfaces, delivering seamless small language model experiences.
- Build Types
- Configure workflow according to actual business:
- Start, End: Built-in input/output modules; customizable input/output parameters and fields;
- Model: Select the model to use in this module, input variables obtained from other modules, edit prompts and output messages, and save as variables;
- Knowledge Base Retrieval: Retrieve the most matching information from the selected knowledge base based on input variables and return it;
- Skill: Select one skill to perform input/output actions through that skill;
- Code: Customize and create code functions based on output variables from other modules;
- Selector: Connect multiple downstream branches; if the set condition is met, only the corresponding branch runs; if none are met, only the "Else" branch runs;
- Intent Recognition: Recognize user input intent and match it with preset intent options;
- Text Formatter: Process formatting of multiple string-type variables;
- Data Source: Select data sources to add referenceable variable content;
- File Retrieval: Search uploaded files to find relevant answers based on input questions;
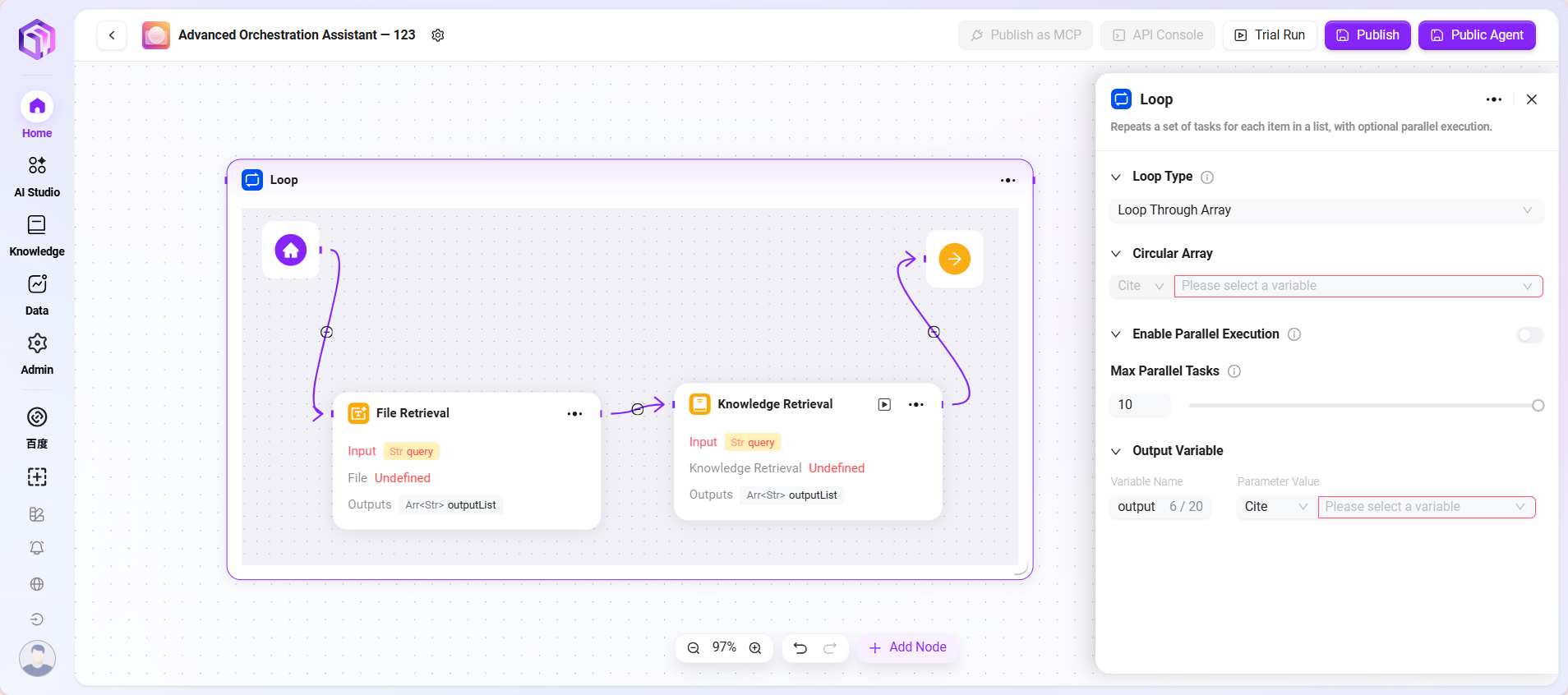
- Loop: Repeat a set of tasks for each item in a list, with optional parallel processing.
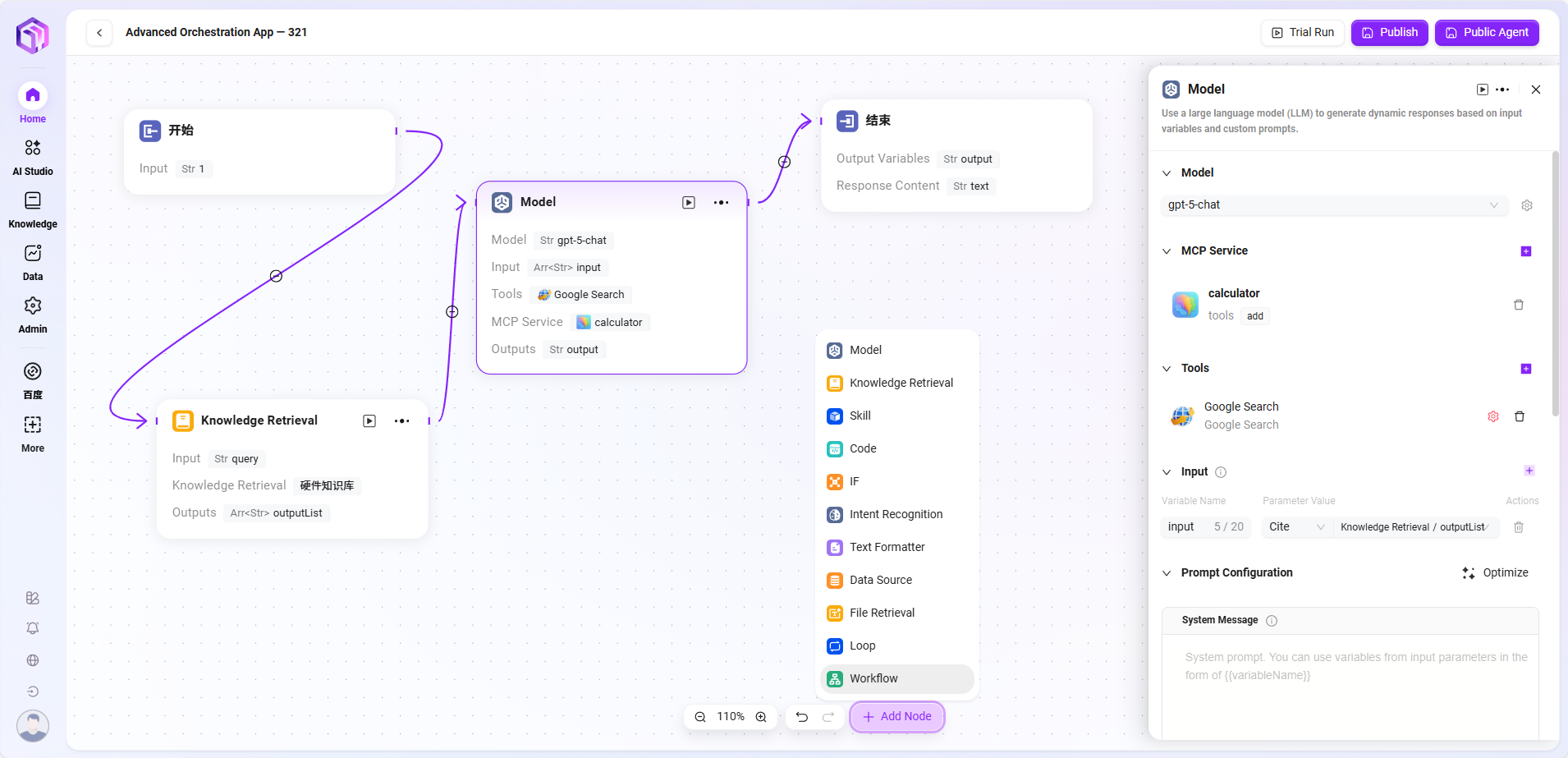
- Detailed Node Introduction
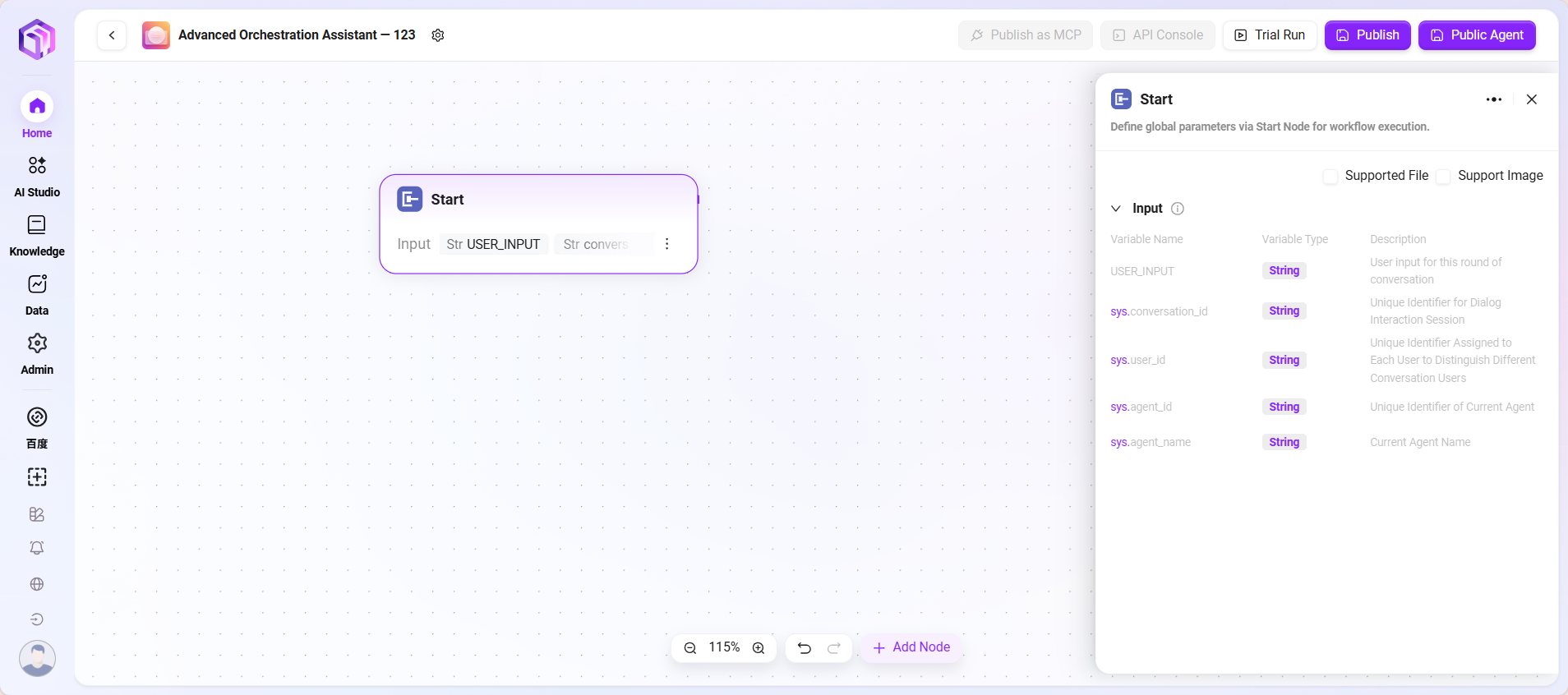
- Start
- Start Node: The starting node of the workflow, used to set the information needed to start the workflow
- Input: Simply put, it tells the LLM in advance what basic information (input parameters) is needed to complete a task. When in use, the LLM remembers these requirements and automatically calls these preset parameters once it detects the task start trigger in the conversation, placing parameters in corresponding positions to start the entire process.
- Processing Logic: Direct pass-through (Bypass), no processing, just passes user input unchanged to the next node.
- Output Result: Outputs all input content directly.
- Model
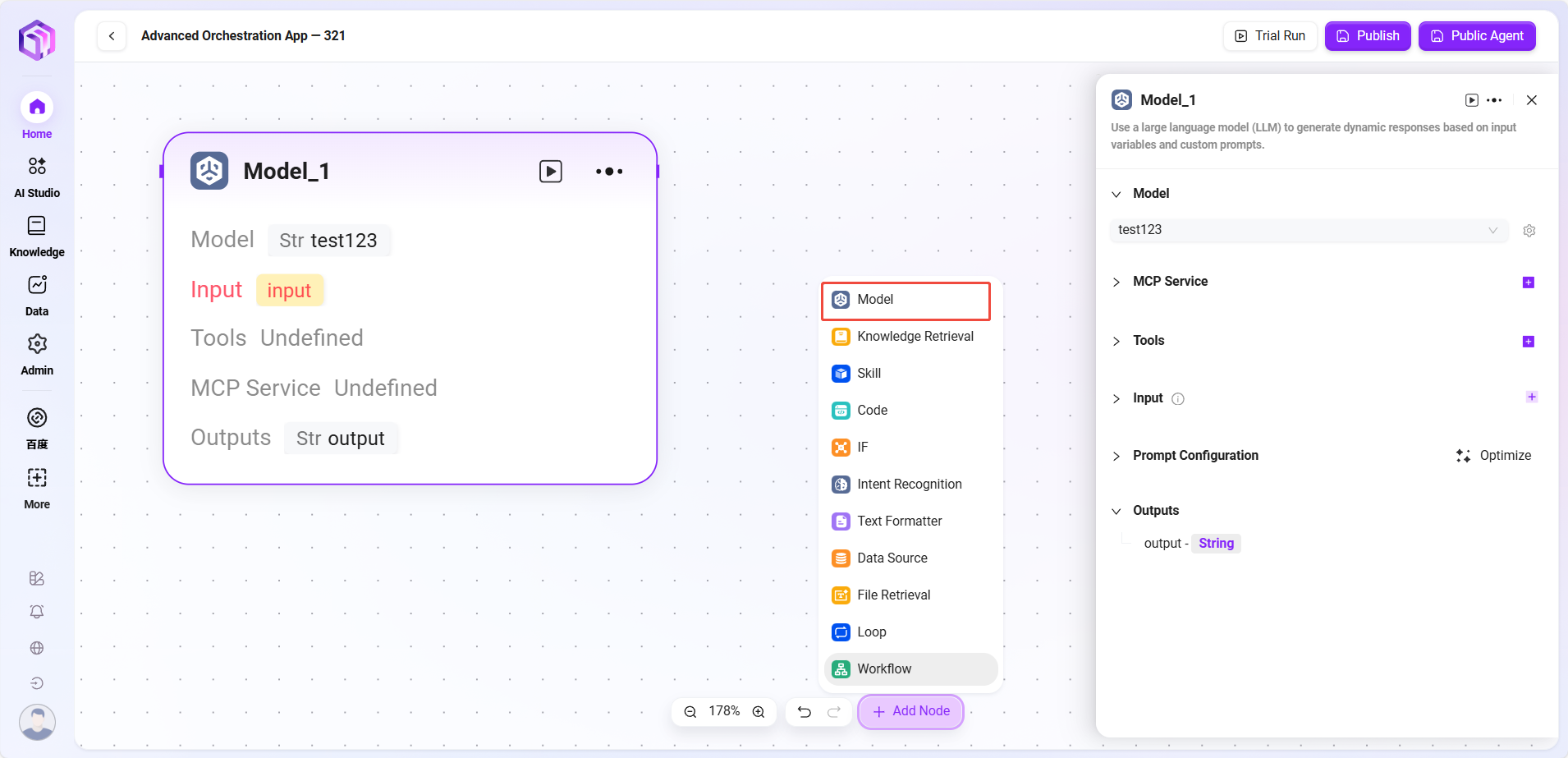
- Model: Calls large language models, uses variables and prompts to generate responses
- Input: Dropdown to select existing models, choose input variable names
- Input Parameters: query (String, from upstream or user input)
- Configuration Parameters:
- One or more Tools
- Model
- GPT (GPT or other models)
- Temperature: Controls creativity; higher values mean more creative and random answers
- Top P: Limits word selection range by "probability threshold," controlling answer diversity
- Max Reply Length: Limits the maximum number of words AI can reply at once
- System Prompt: Hidden instructions given to AI to control overall style
- User Prompt: User input content or questions
- History: Previous conversation turns to maintain context understanding
- Processing Logic: Passes input to the LLM for processing; model generates answers based on configuration
- Output Result: Text content generated by the model
💡 Tip: You need to connect to a preceding node first to select variables from other nodes as input variables for the current node.
-
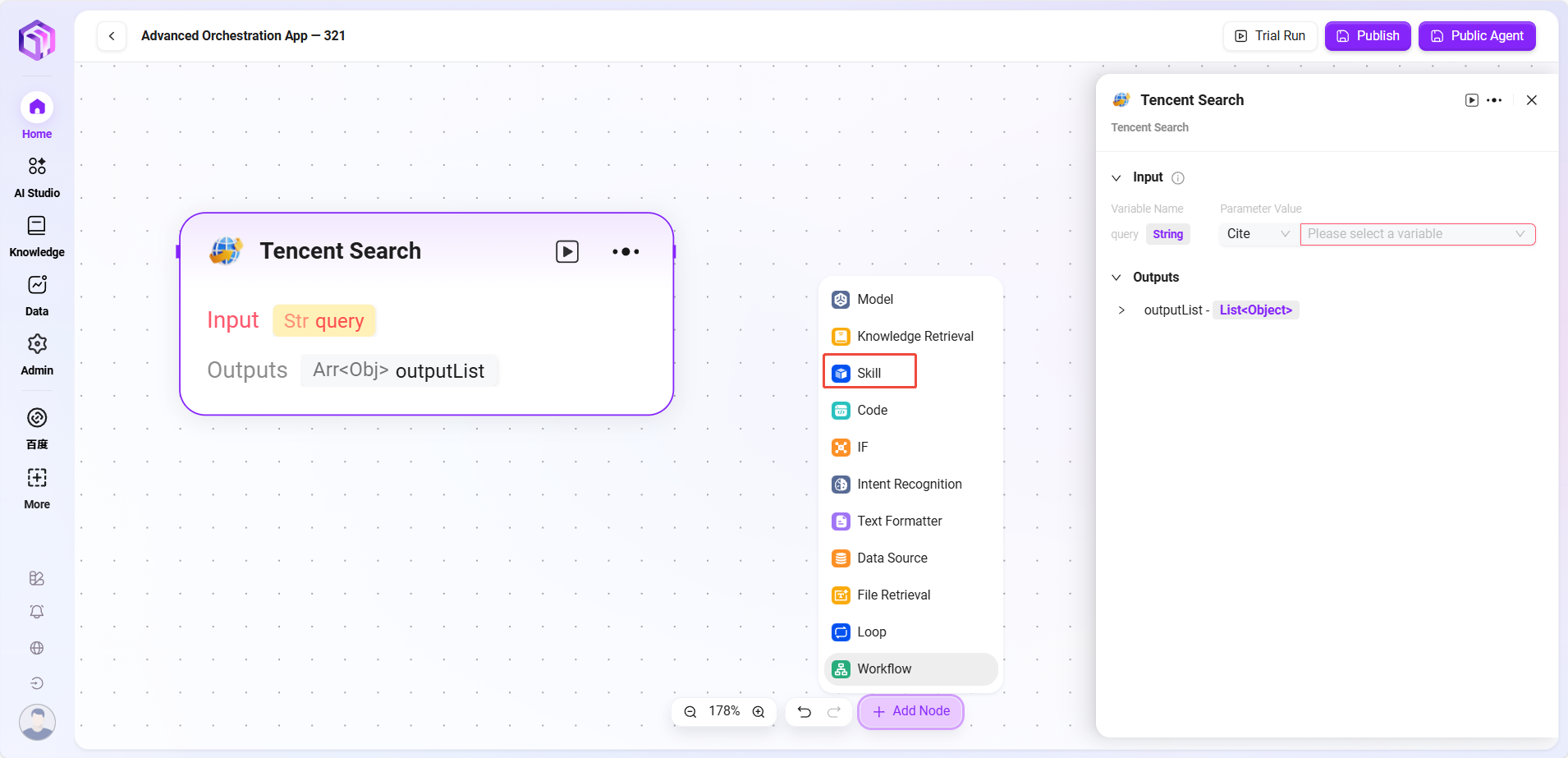
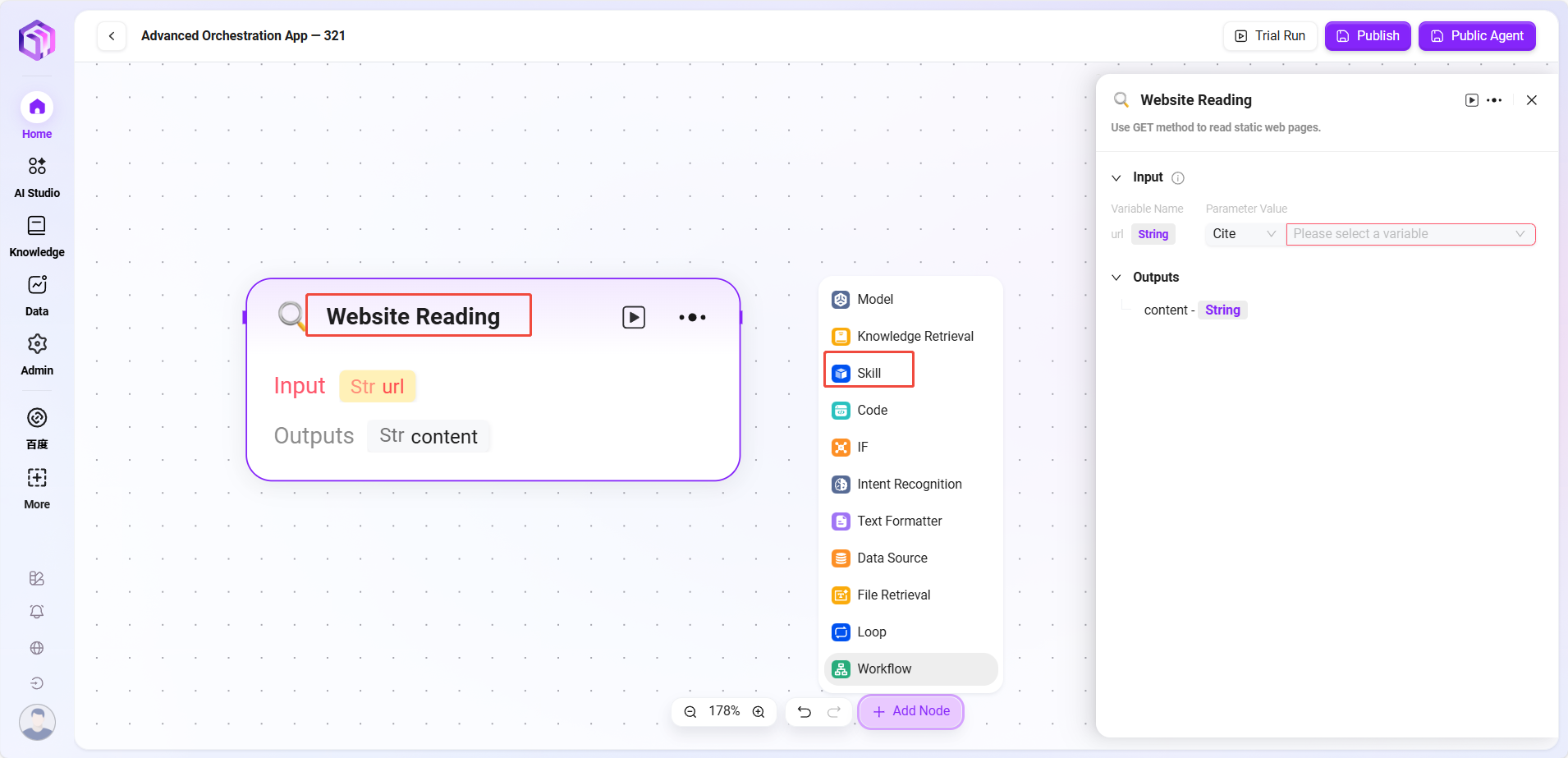
Skills (some examples)
- Website Reader: Can read static text on web pages (but cannot see dynamically loaded content).
- Text-to-Image: Converts a piece of text into an image (outputs image URL).
- Tencent Search: Calls search engine to return search results.
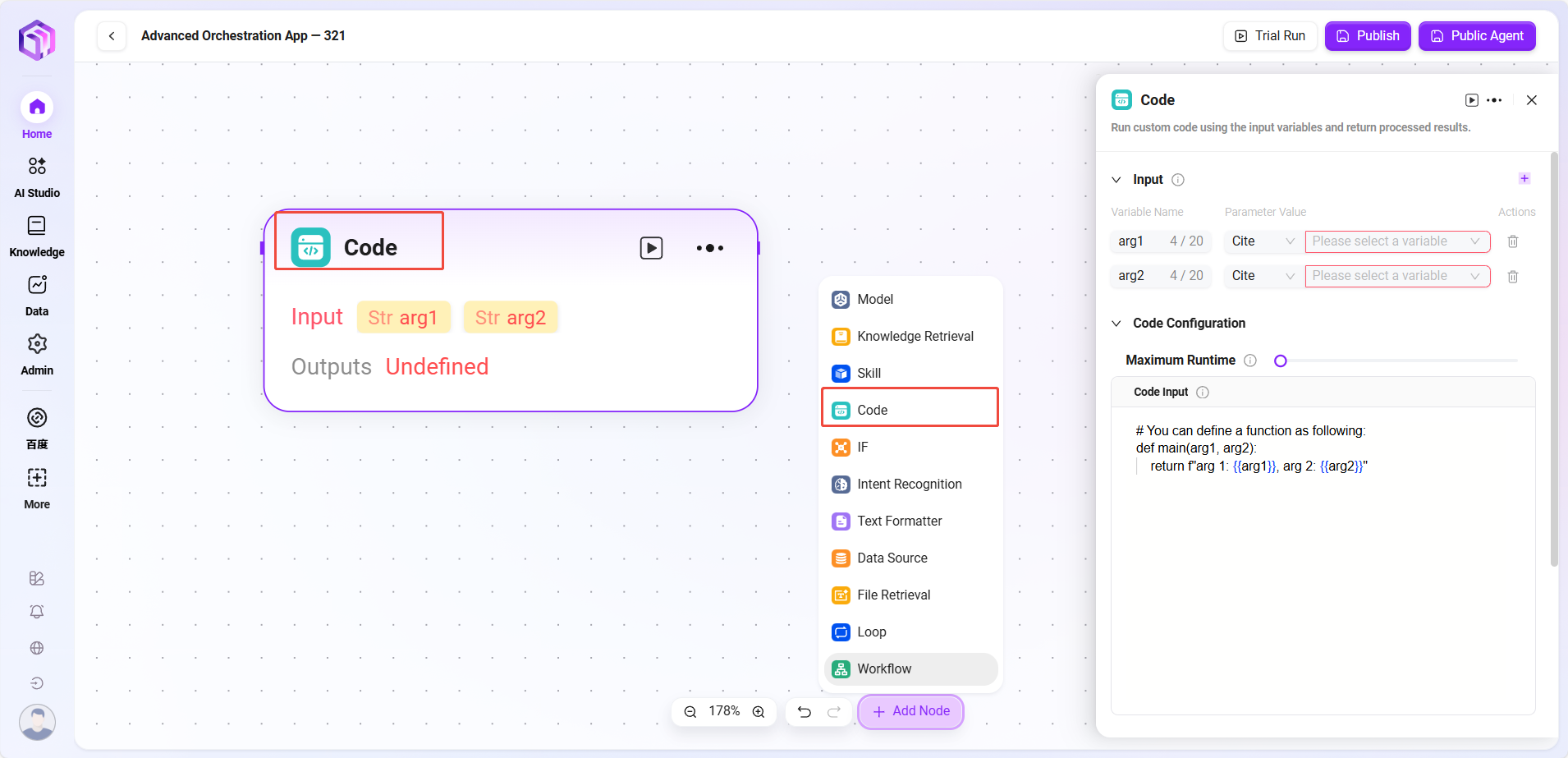
- Code
- Code: Write code to process input variables and generate return values
- Input: Receives externally passed variables, serving as data entry for code execution and providing raw data for subsequent processing
- Input Parameters: query (string, code request from user or upstream)
- Configuration Parameters: Settings related to code execution
- Maximum Runtime
- Code Content (Code Input)
- Processing Logic:
- Runs code in a secure sandbox environment (based on RestrictedPython or designated platform)
- Limits runtime and access permissions to avoid security risks
- Output Result: After processing input data, outputs results as specified variables, serving as the exit for code processing results
-
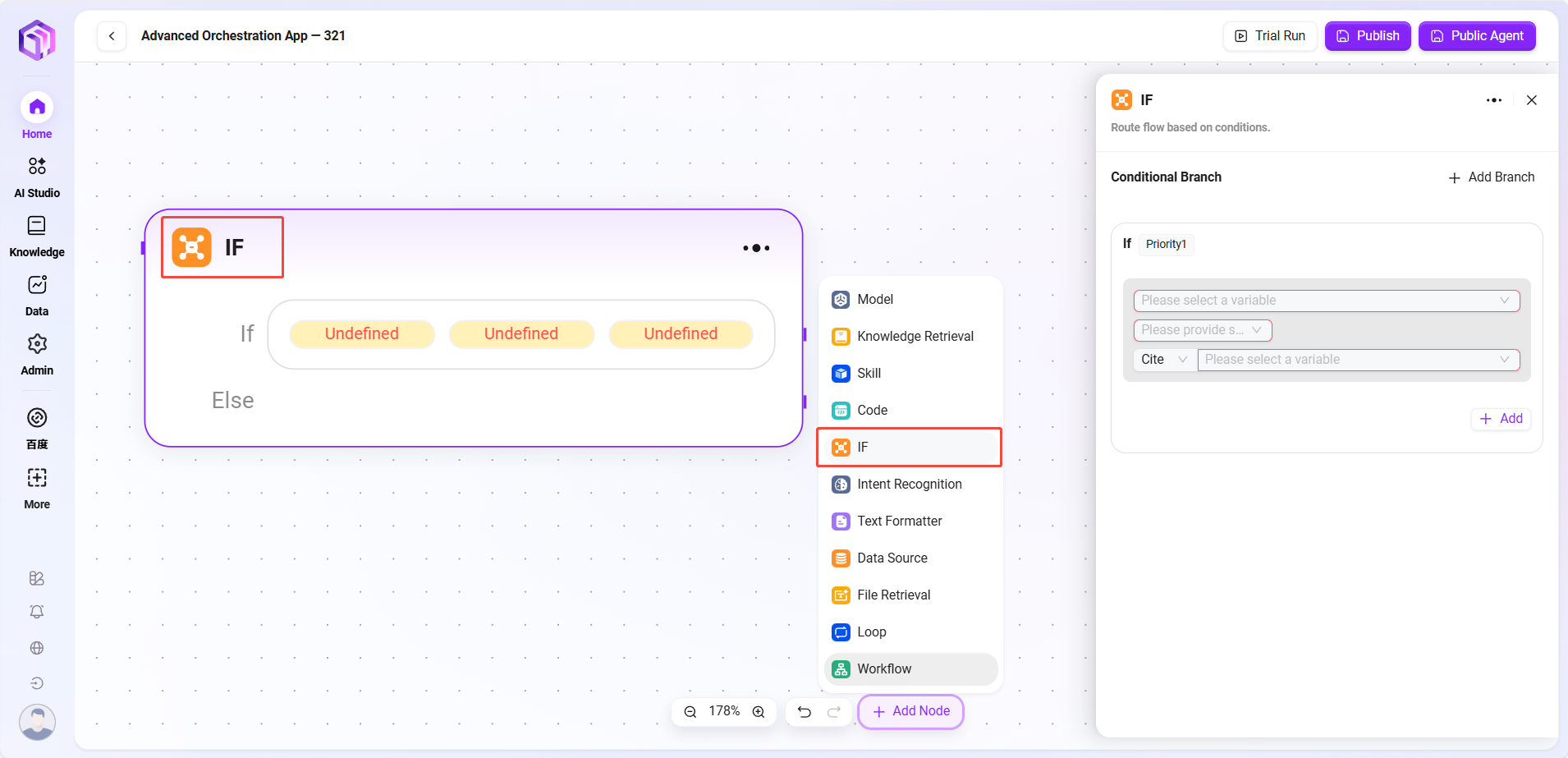
Selector
- Selector: Acts as a conditional judgment in workflow orchestration. It connects multiple downstream branches and decides execution paths based on set conditions.
- Conditional Branches: Multiple conditions can be set, e.g., "if - priority 1." By configuring referenced variables, selecting conditions (e.g., equals, greater than), and comparison values, it judges whether conditions are met. If met, runs the corresponding branch.
- Processing Logic: Routes to different paths based on conditions (if none met, goes to Else)
- Output Result: No direct output; only determines the next node's direction
-
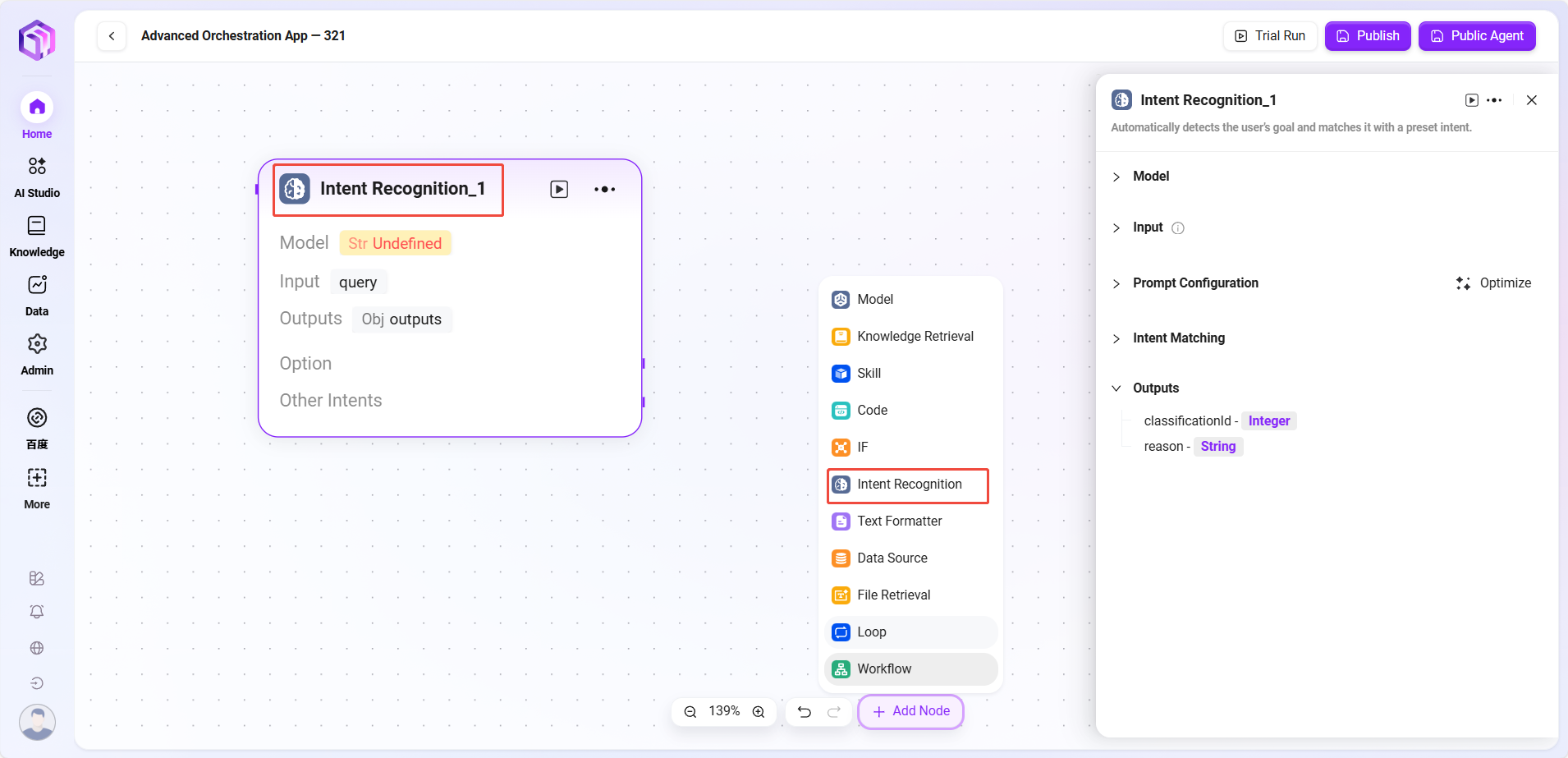
Intent Recognition
- Intent Recognition: A key part of natural language processing; this module analyzes user input to determine true intent and match preset options
- Model: Selects the model used for intent recognition, which determines capability and effectiveness
- Intent Matching: User intent descriptions can be pre-input as matching criteria; new intents can also be added. The system judges which preset intent matches user input.
- Advanced Settings: Can set system prompt content, referencing input variables to optimize prompt effect; can also set history memory count for the model to reference past conversations to improve recognition accuracy
- Processing Logic: Determines user's true intent and classifies input into corresponding categories
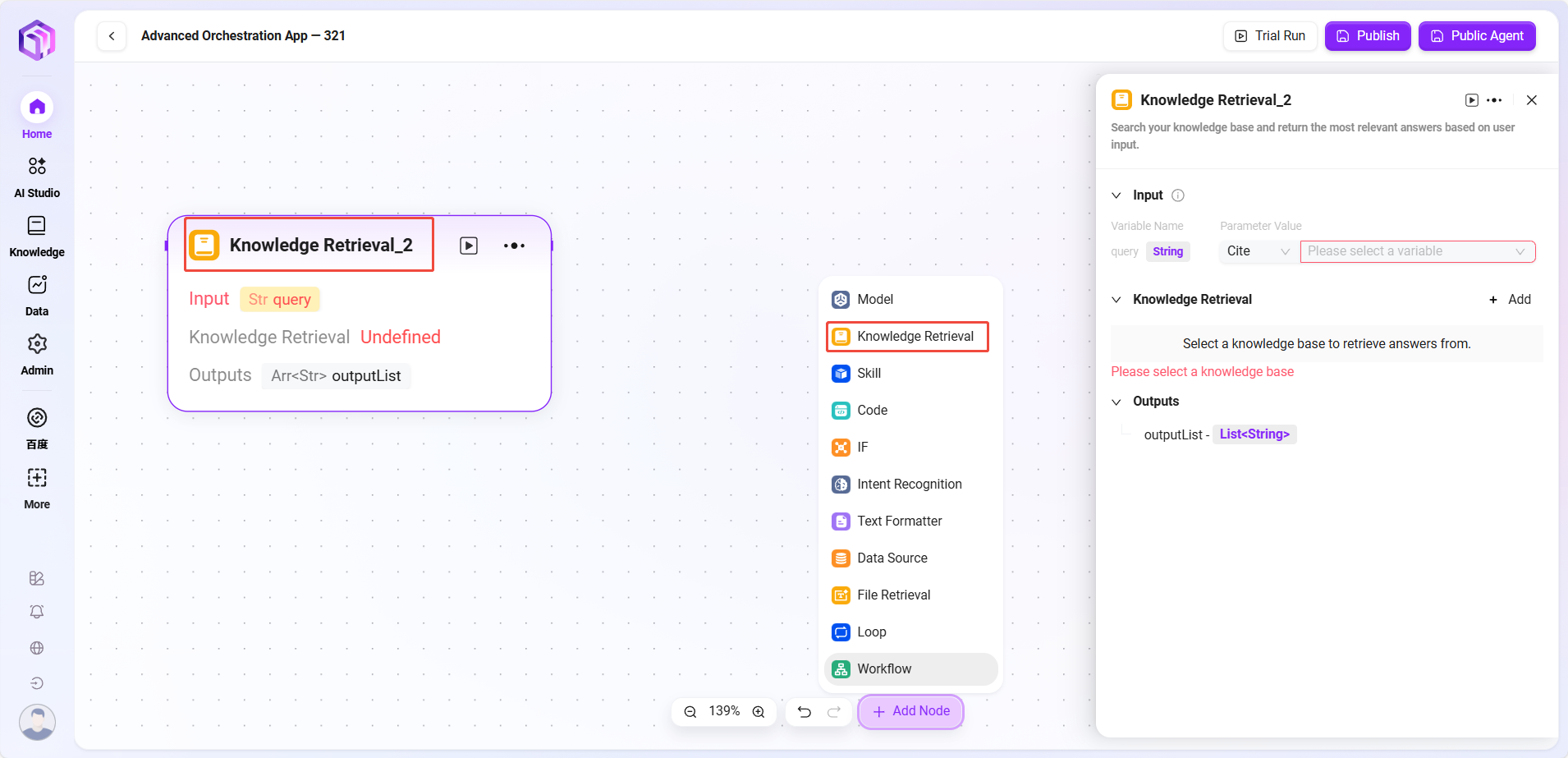
- Knowledge Base Retrieval
- Input: Defines variable names and sets parameter values to provide retrieval keywords and other raw data for knowledge base search
- Processing Logic: Searches the knowledge base based on input and parameters, returning fragments or FAQs
- Knowledge Base: Selects a specific knowledge base as the search scope; the system searches within this scope for matching information
- Maximum Recall Count: Sets the maximum number of matching results returned from the knowledge base to avoid excessive data
- Output: Outputs matched information retrieved from the knowledge base as specified variables for subsequent workflow use
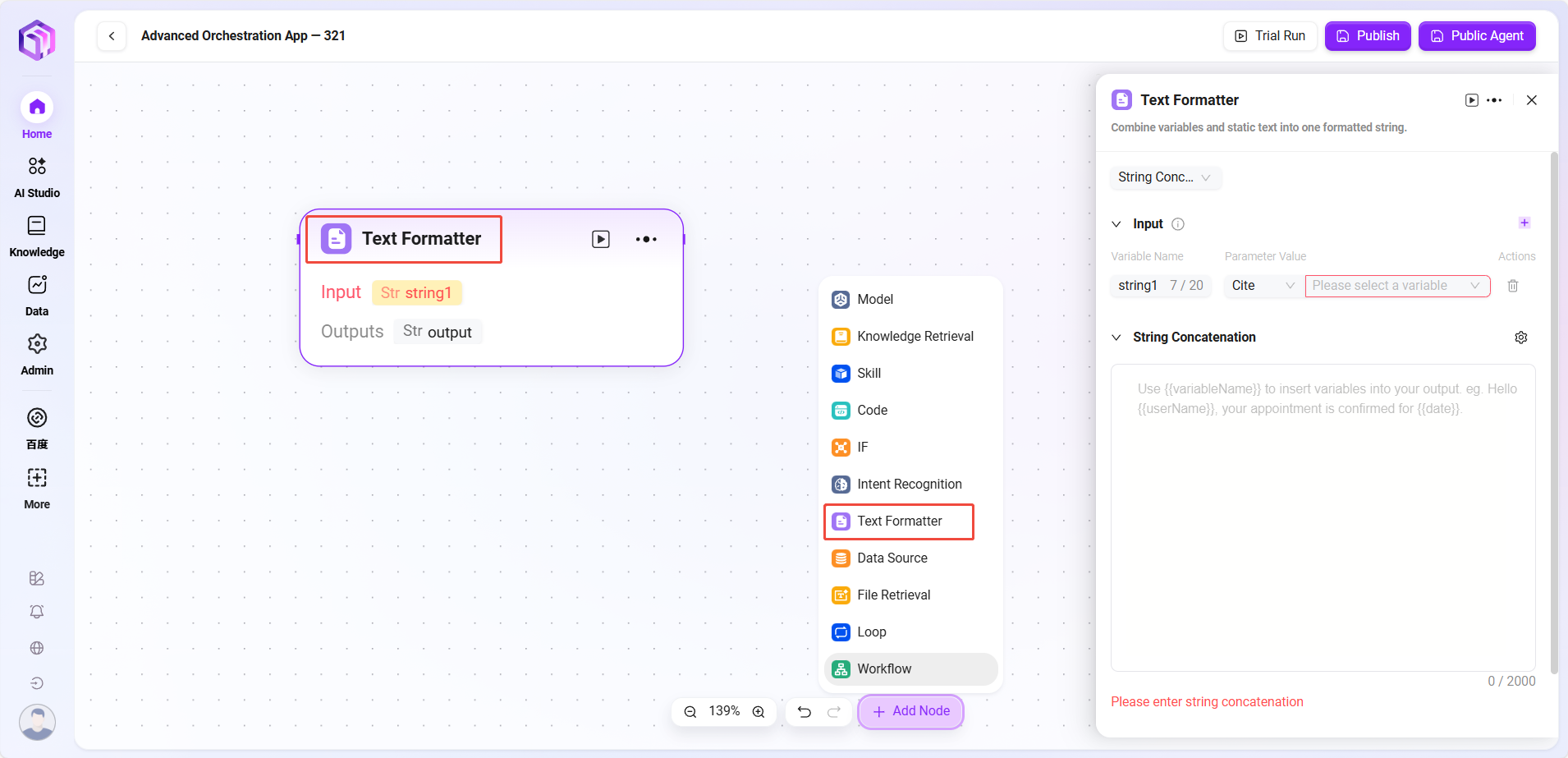
- Text Formatter
- Text: Mainly used to process string-type variable formats
- Input: Defines variable names and references parameter values to provide raw string data for subsequent text processing
- Processing Logic: Performs simple text processing
- String concatenation
- String splitting
- String Concatenation: Provides a text editing area where input variables can be referenced by variable names as needed to concatenate multiple strings or format them
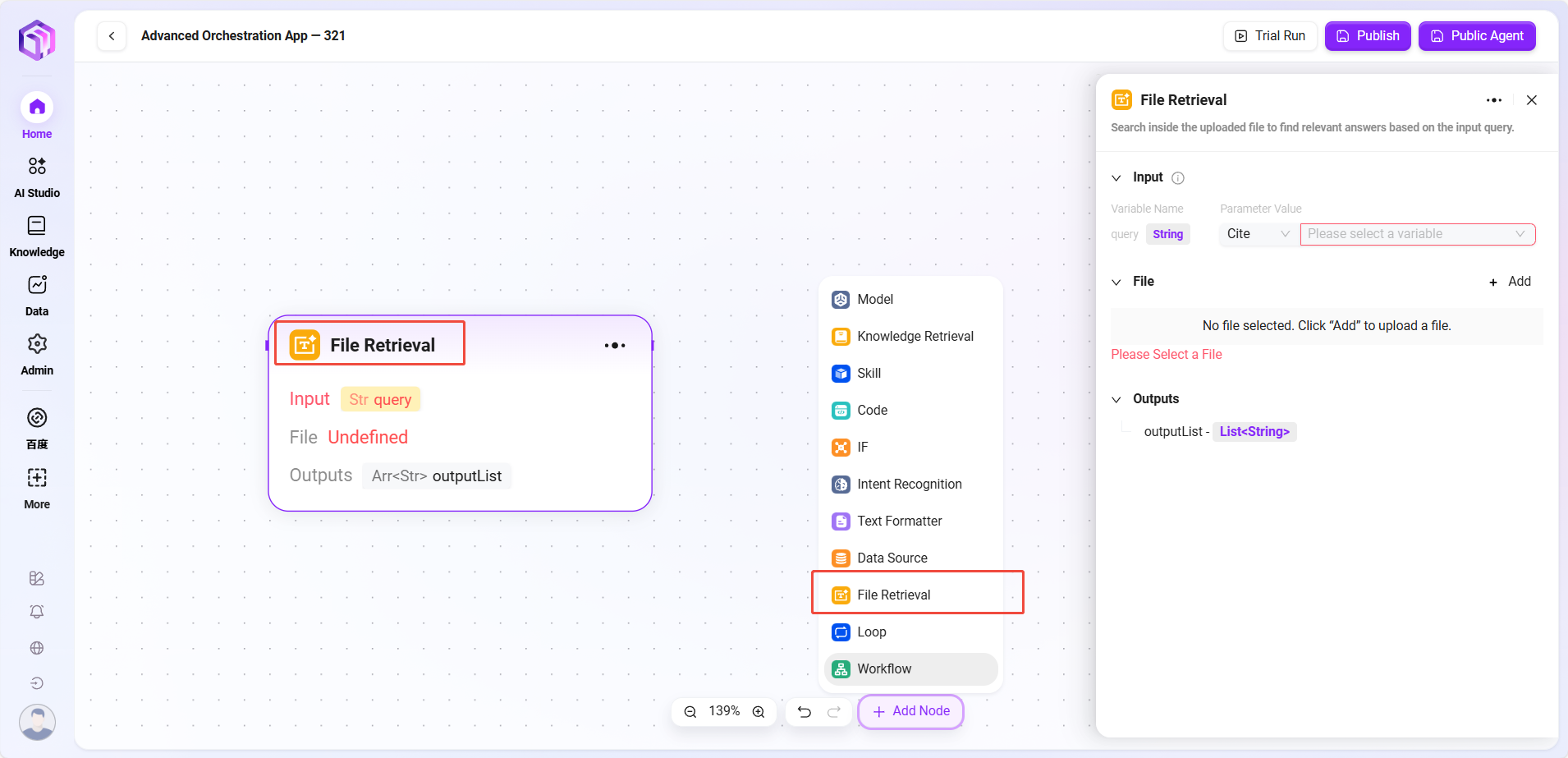
- File Retrieval
- File Retrieval: A functional module for searching and operating on file content
- Input: Defines variable names and references parameter values to provide search keywords and other input information as basis for file content search
- File: Files to be processed can be added to this node to determine the search scope
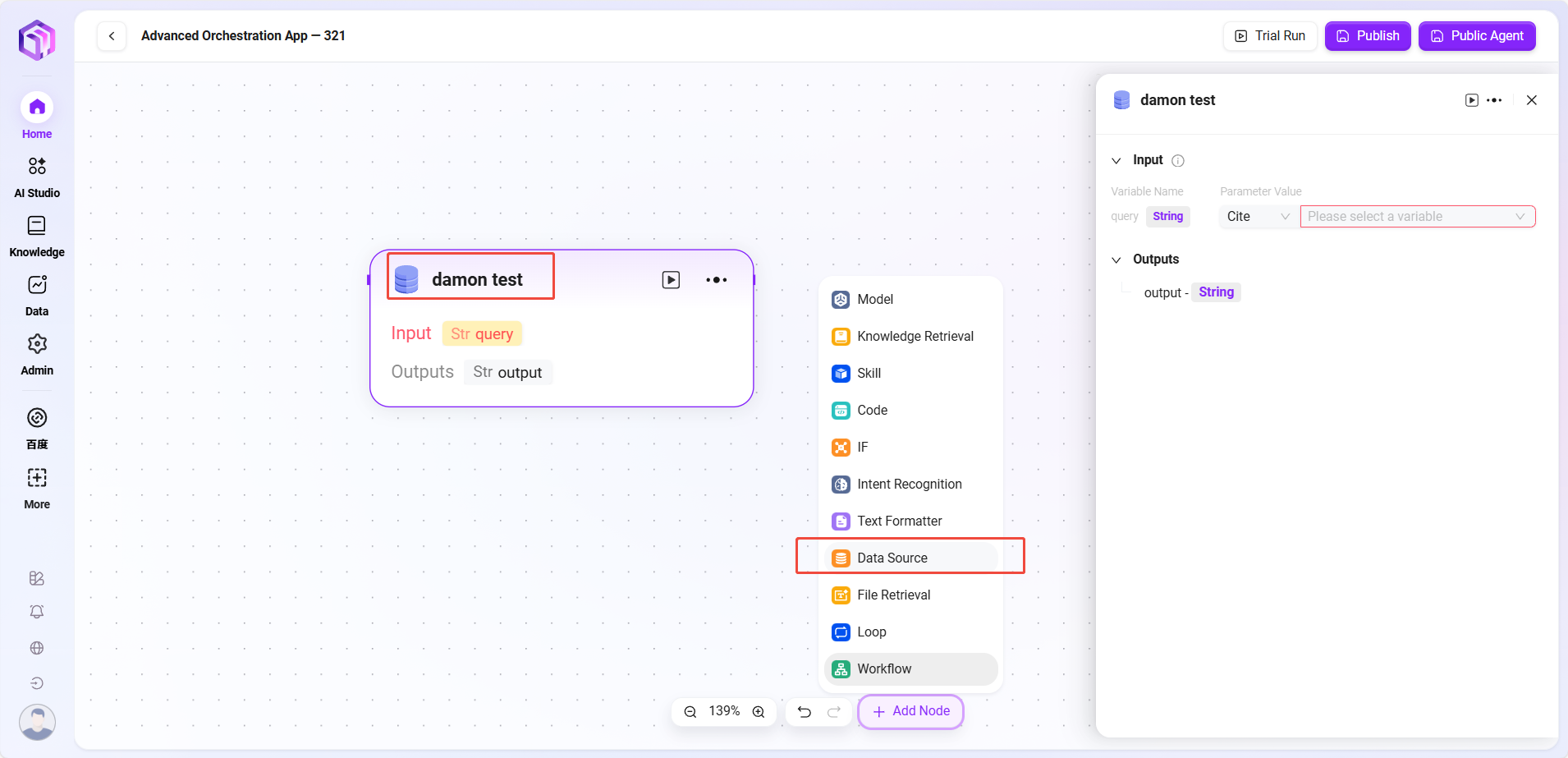
- Data Source
- Data Source: Selects the data source to connect
- Processing Logic: Converts natural language into SQL to query the database and returns results
- Output: Outputs data from the data source to the next node.
- Loop
- Loop Node: Used to repeatedly execute a set of tasks a specified number of times or over a specified data collection. Different loop modes can flexibly implement batch processing or repeated operations.
- Loop Types: Supports two modes
- Use array loop: Executes tasks sequentially for each element in the input array.
- Use numeric loop: Executes tasks according to the set number of times.
- Loop Count/Array:
- When "numeric loop" is selected, a specific number must be input, e.g., 2, meaning the task will be executed twice.
- When "array loop" is selected, an array variable must be provided; the system takes elements one by one as input to execute tasks.
- Parallel Execution: Optional. If enabled, the system processes multiple loop tasks simultaneously to improve efficiency. Users can set the maximum parallel count to control resource usage.
Workflow Example
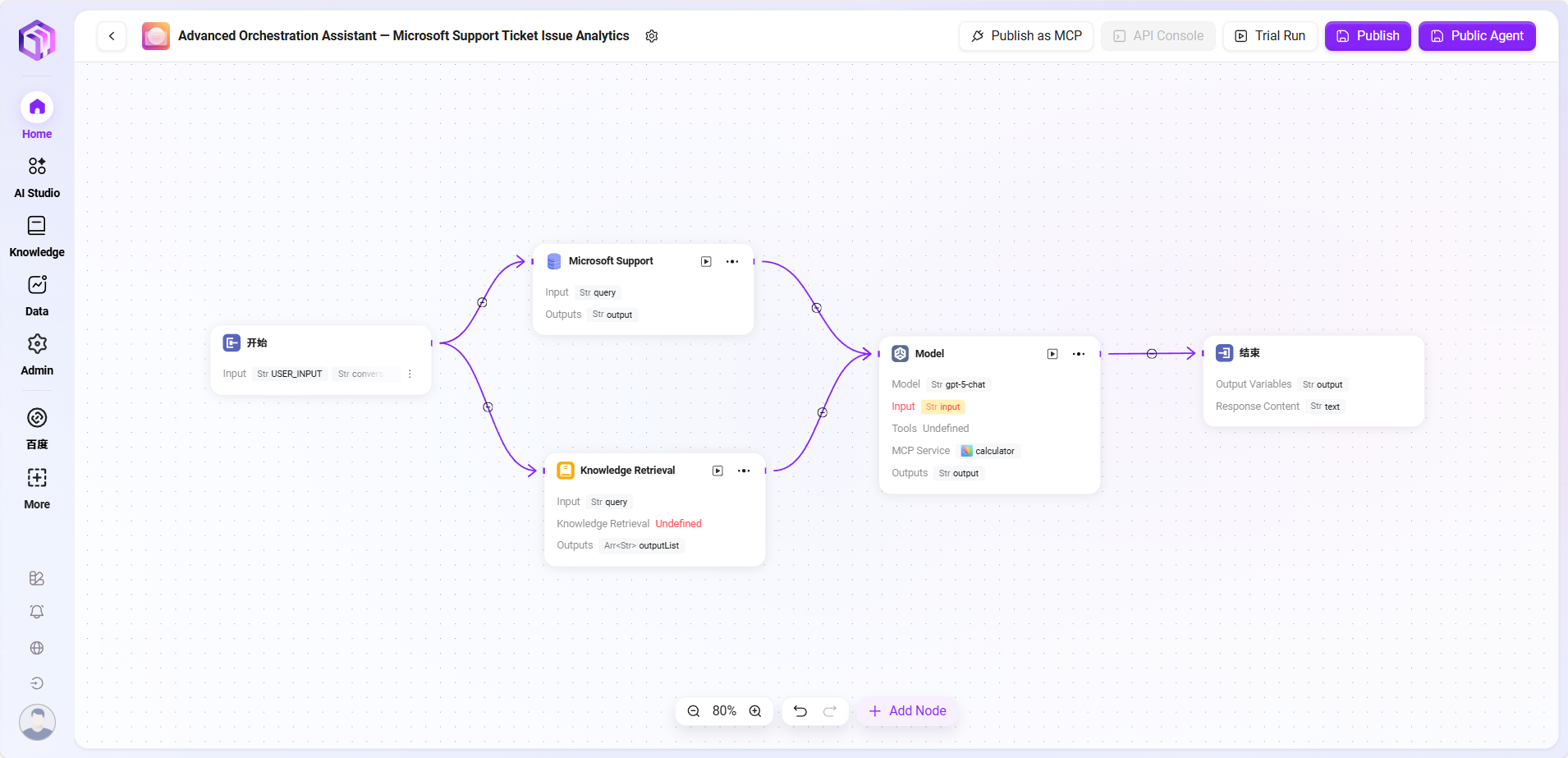
In this scenario, the workflow function is used to build a complete "Microsoft Support Ticket Issue Analytics" process, with the following steps:
- Start Node
The starting point of the process, included by default. - Data Source Node
Connects the raw data needed for ticket analysis. - Knowledge Base Node
Connects knowledge documents containing analysis reference materials, serving as theoretical support for AI analysis. - Model Node
Based on AI models, combines data source and knowledge base content for comprehensive analysis, generating ticket issue analysis results. - End Node
The endpoint of the process, outputs the analysis results from the model node. This node is included by default.
The data source node and knowledge base node are configured in parallel, while the model node aggregates information from both to ensure output results have data basis and theoretical support.
The final effect is as follows:
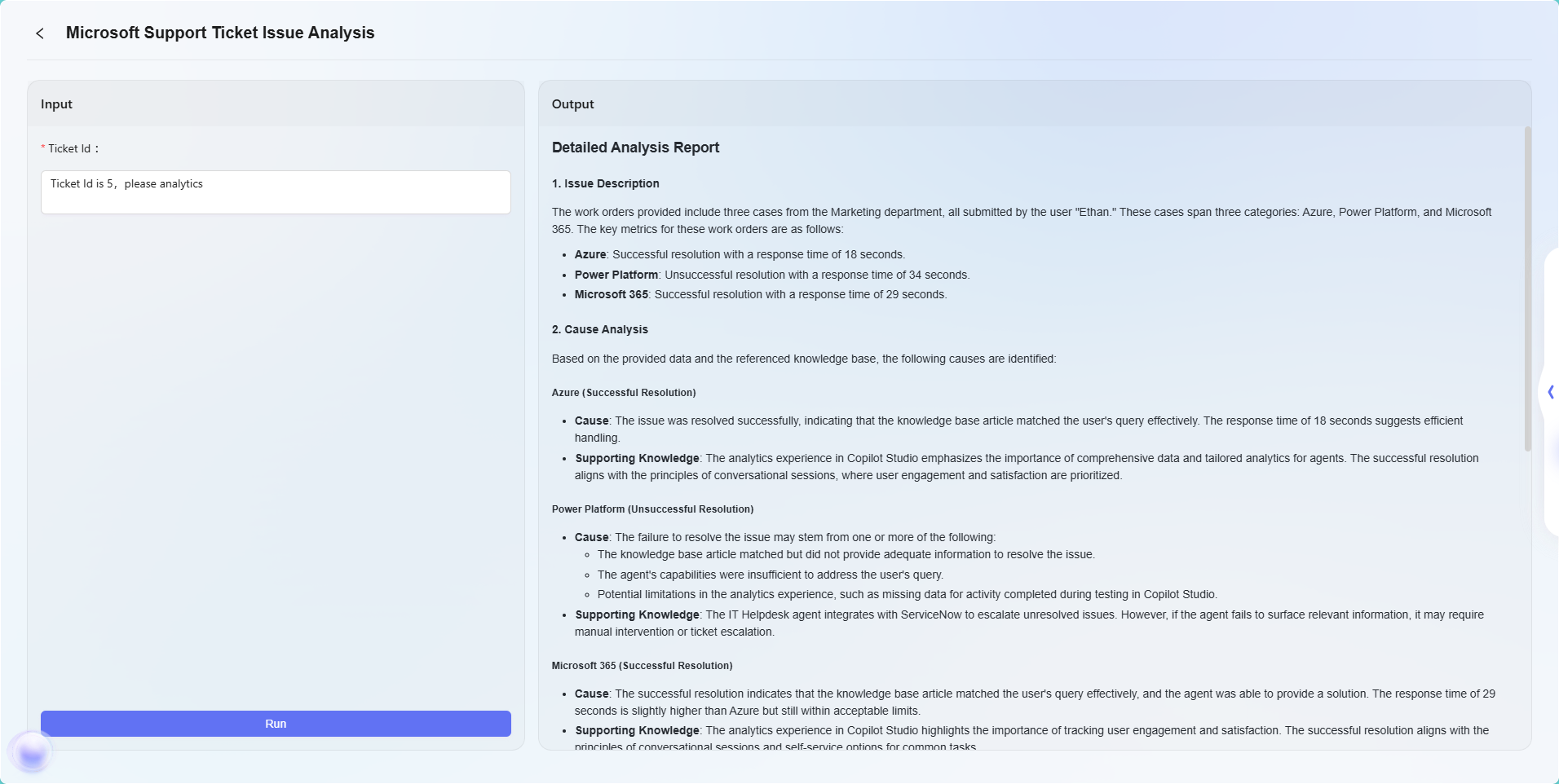
Note: This example is a simple application of the advanced orchestration feature to demonstrate its basic workflow effect. Advanced orchestration has powerful flexibility and extensibility, supporting complex business logic and intelligent automation workflows through various node types, and can be widely applied in many real business scenarios.
What is MCP
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is the core extension protocol of the Agent platform, responsible for connecting external tools, data sources, and services, providing powerful capability extension support for AI assistants.
Functional Modules
| Function Category | Main Purpose |
|---|---|
| Computing Service | Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulo, square root, exponentiation |
| Search Service | Web search, academic paper retrieval, data extraction |
| Data Analysis | Chart generation, analytical capabilities |
| Tool Integration | Map services, collaboration tool integration |
How to Create a Personal MCP
-
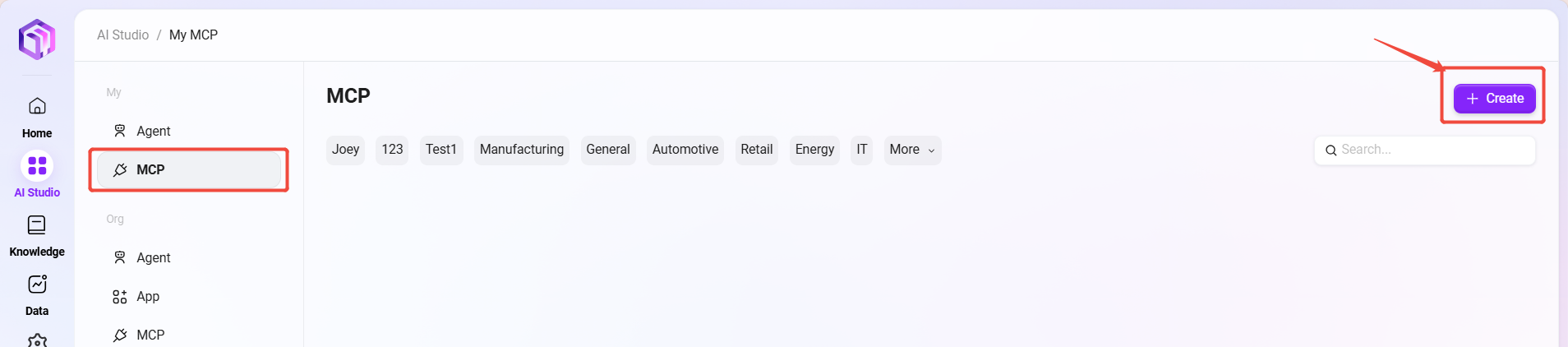
On the AI Studio page's left sidebar, click "MCP" to enter the MCP page;
-
After entering the MCP page, click the "Create" button at the top right to enter the MCP creation page;
-
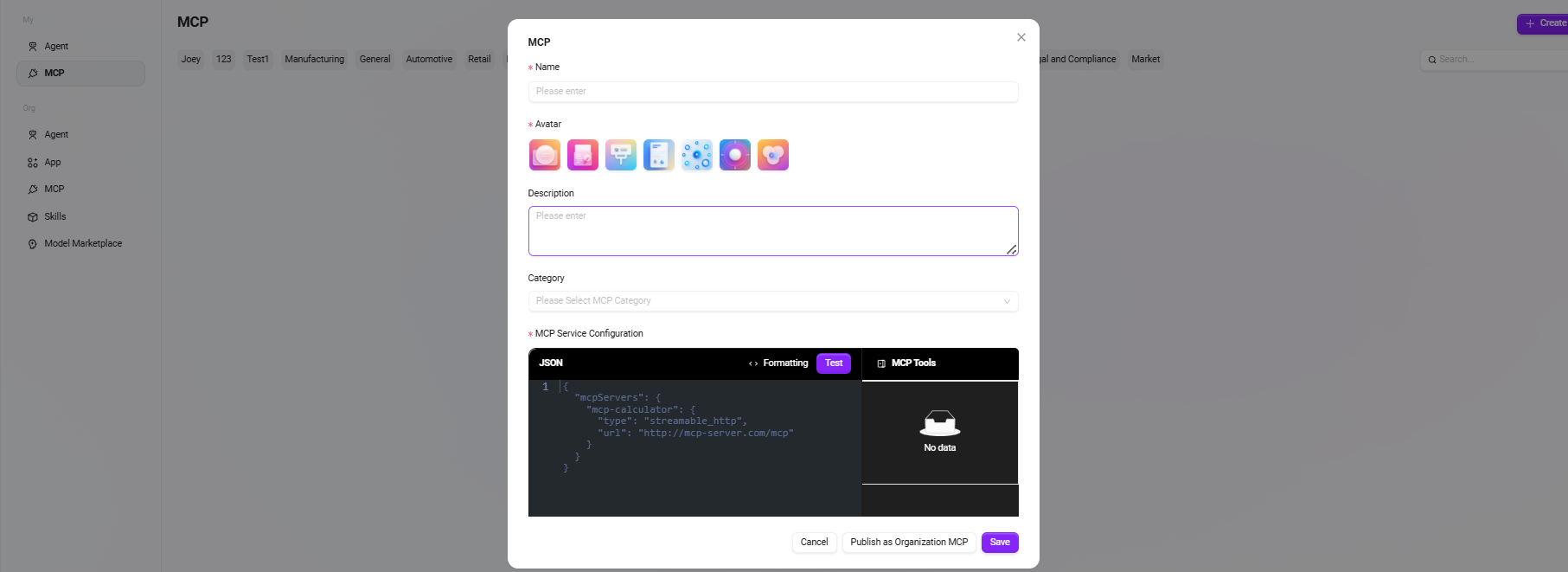
Fill in basic information
- MCP Name: Enter the MCP's name as its identifier.
- MCP Avatar: Select the default avatar; uploading avatars is currently not supported.
- MCP Description: Briefly describe the MCP's functional features and main purposes.
- MCP Category: Select the category where the new MCP belongs.
- MCP Service Configuration: Register external services via JSON code to grant new capabilities to the assistant.